BREEDS: Benchmarks for Subpopulation Shift
Paper and Code
Aug 11, 2020
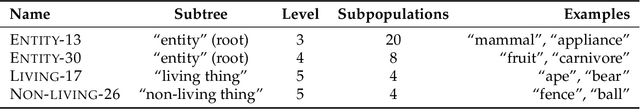

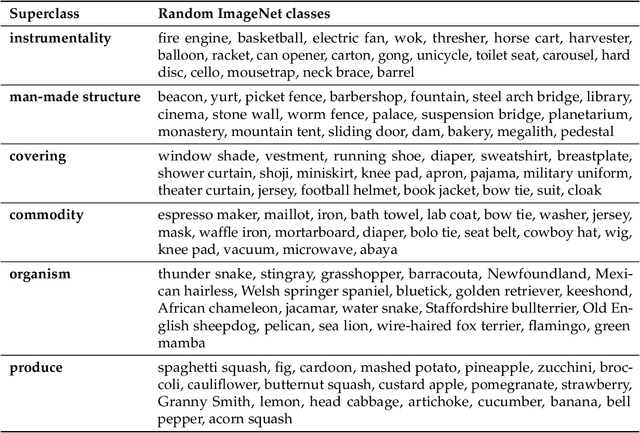
We develop a methodology for assessing the robustness of models to subpopulation shift---specifically, their ability to generalize to novel data subpopulations that were not observed during training. Our approach leverages the class structure underlying existing datasets to control the data subpopulations that comprise the training and test distributions. This enables us to synthesize realistic distribution shifts whose sources can be precisely controlled and characterized, within existing large-scale datasets. Applying this methodology to the ImageNet dataset, we create a suite of subpopulation shift benchmarks of varying granularity. We then validate that the corresponding shifts are tractable by obtaining human baselines for them. Finally, we utilize these benchmarks to measure the sensitivity of standard model architectures as well as the effectiveness of off-the-shelf train-time robustness interventions. Code and data available at https://github.com/MadryLab/BREEDS-Benchmarks .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge