Branching Time Active Inference with Bayesian Filtering
Paper and Code
Dec 14, 2021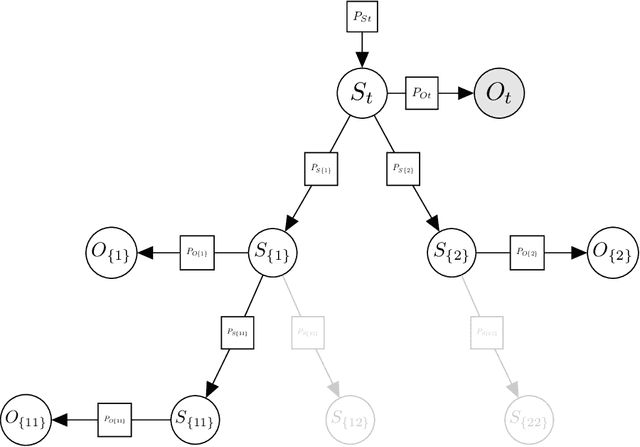
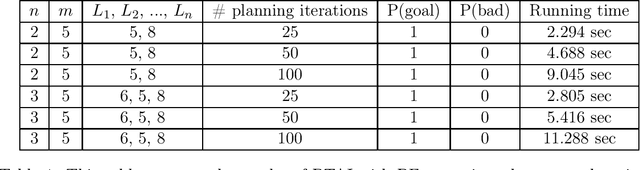
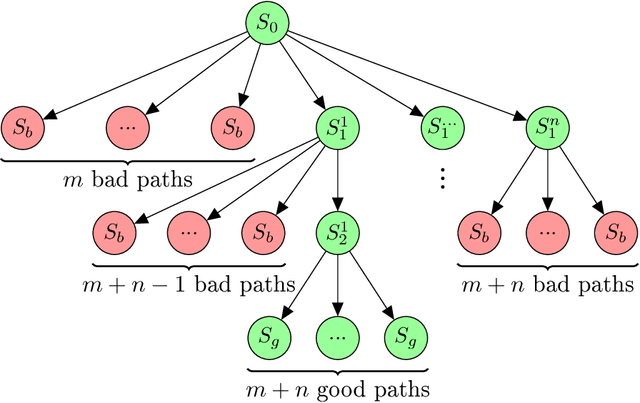
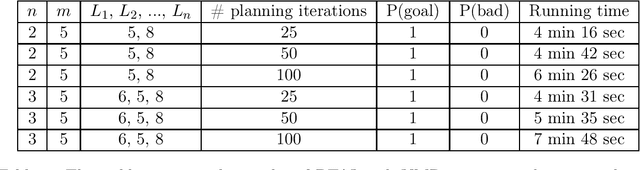
Branching Time Active Inference (Champion et al., 2021b,a) is a framework proposing to look at planning as a form of Bayesian model expansion. Its root can be found in Active Inference (Friston et al., 2016; Da Costa et al., 2020; Champion et al., 2021c), a neuroscientific framework widely used for brain modelling, as well as in Monte Carlo Tree Search (Browne et al., 2012), a method broadly applied in the Reinforcement Learning literature. Up to now, the inference of the latent variables was carried out by taking advantage of the flexibility offered by Variational Message Passing (Winn and Bishop, 2005), an iterative process that can be understood as sending messages along the edges of a factor graph (Forney, 2001). In this paper, we harness the efficiency of an alternative method for inference called Bayesian Filtering (Fox et al., 2003), which does not require the iteration of the update equations until convergence of the Variational Free Energy. Instead, this scheme alternates between two phases: integration of evidence and prediction of future states. Both of those phases can be performed efficiently and this provides a seventy times speed up over the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge