Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2019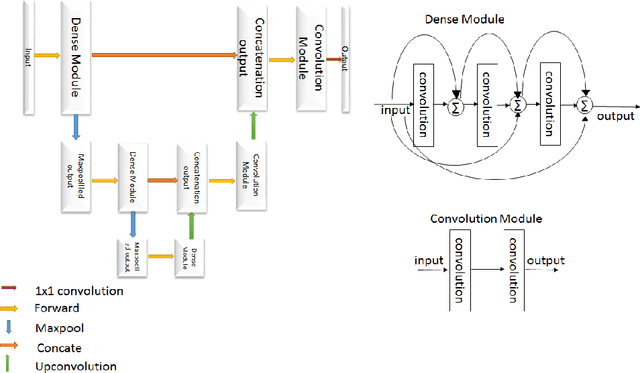
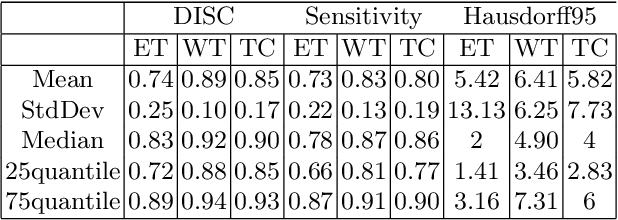
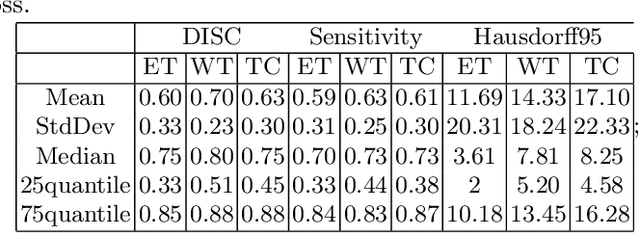
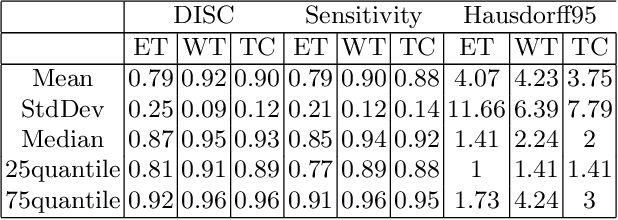
The paper demonstrates the use of the fully convolutional neural network for glioma segmentation on the BraTS 2019 dataset. Three-layers deep encoder-decoder architecture is used along with dense connection at encoder part to propagate the information from coarse layer to deep layers. This architecture is used to train three tumor sub-components separately. Subcomponent training weights are initialized with whole tumor weights to get the localization of the tumor within the brain. At the end, three segmentation results were merged to get the entire tumor segmentation. Dice Similarity of training dataset with focal loss implementation for whole tumor, tumor core and enhancing tumor is 0.92, 0.90 and 0.79 respectively. Radiomic features along with segmentation results and age are used to predict the overall survival of patients using random forest regressor to classify survival of patients in long, medium and short survival classes. 55.4% of classification accuracy is reported for training dataset with the scans whose resection status is gross-total resection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge