Bootstrapping Transliteration with Constrained Discovery for Low-Resource Languages
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2018
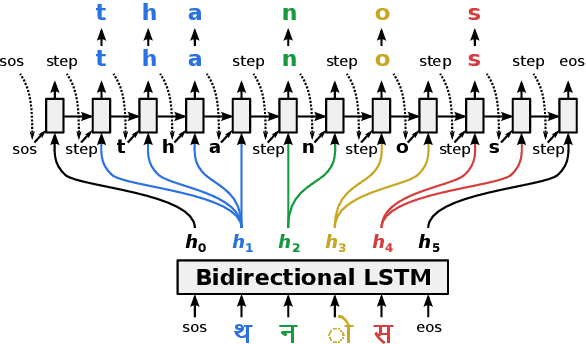

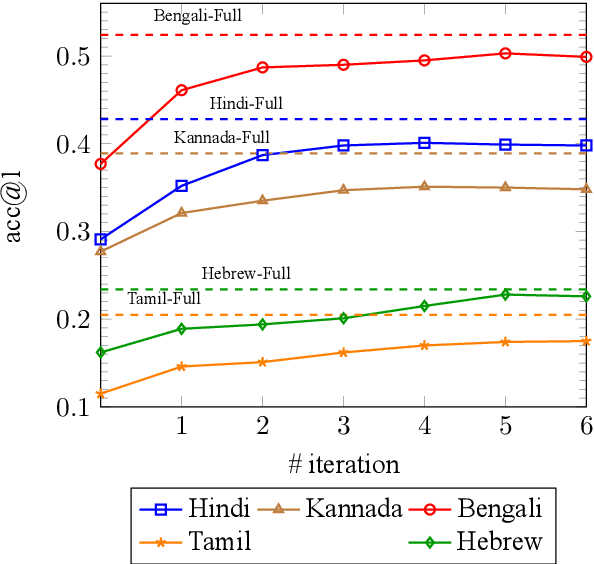
Generating the English transliteration of a name written in a foreign script is an important and challenging step in multilingual knowledge acquisition and information extraction. Existing approaches to transliteration generation require a large (>5000) number of training examples. This difficulty contrasts with transliteration discovery, a somewhat easier task that involves picking a plausible transliteration from a given list. In this work, we present a bootstrapping algorithm that uses constrained discovery to improve generation, and can be used with as few as 500 training examples, which we show can be sourced from annotators in a matter of hours. This opens the task to languages for which large number of training examples are unavailable. We evaluate transliteration generation performance itself, as well the improvement it brings to cross-lingual candidate generation for entity linking, a typical downstream task. We present a comprehensive evaluation of our approach on nine languages, each written in a unique script.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge