Bootstrapping Techniques for Polysynthetic Morphological Analysis
Paper and Code
May 03, 2020
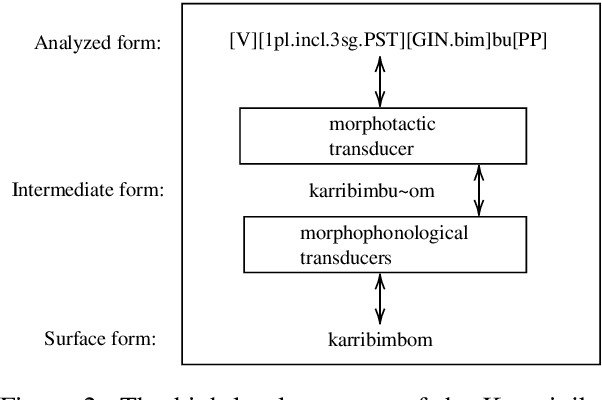
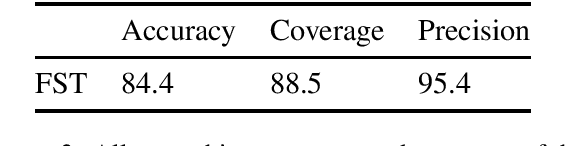
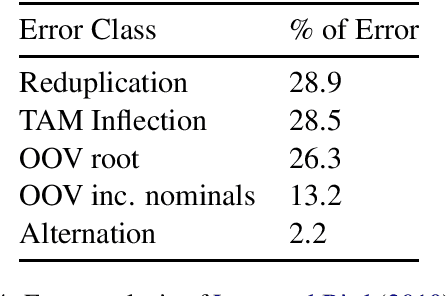
Polysynthetic languages have exceptionally large and sparse vocabularies, thanks to the number of morpheme slots and combinations in a word. This complexity, together with a general scarcity of written data, poses a challenge to the development of natural language technologies. To address this challenge, we offer linguistically-informed approaches for bootstrapping a neural morphological analyzer, and demonstrate its application to Kunwinjku, a polysynthetic Australian language. We generate data from a finite state transducer to train an encoder-decoder model. We improve the model by "hallucinating" missing linguistic structure into the training data, and by resampling from a Zipf distribution to simulate a more natural distribution of morphemes. The best model accounts for all instances of reduplication in the test set and achieves an accuracy of 94.7% overall, a 10 percentage point improvement over the FST baseline. This process demonstrates the feasibility of bootstrapping a neural morph analyzer from minimal resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge