Blind Dates: Examining the Expression of Temporality in Historical Photographs
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2023
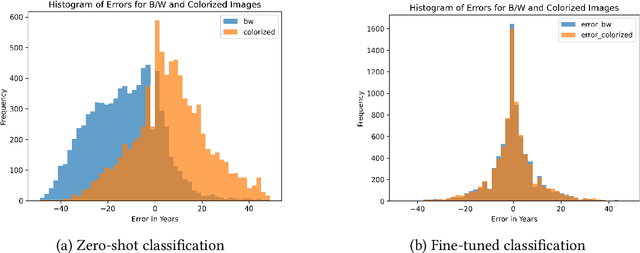

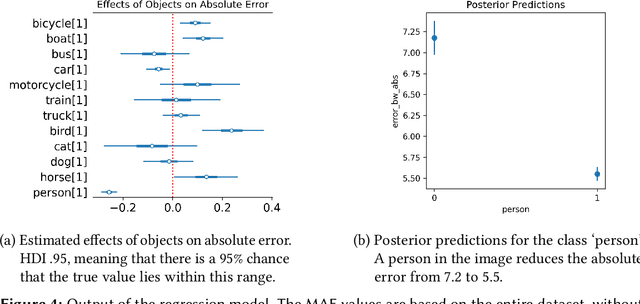
This paper explores the capacity of computer vision models to discern temporal information in visual content, focusing specifically on historical photographs. We investigate the dating of images using OpenCLIP, an open-source implementation of CLIP, a multi-modal language and vision model. Our experiment consists of three steps: zero-shot classification, fine-tuning, and analysis of visual content. We use the \textit{De Boer Scene Detection} dataset, containing 39,866 gray-scale historical press photographs from 1950 to 1999. The results show that zero-shot classification is relatively ineffective for image dating, with a bias towards predicting dates in the past. Fine-tuning OpenCLIP with a logistic classifier improves performance and eliminates the bias. Additionally, our analysis reveals that images featuring buses, cars, cats, dogs, and people are more accurately dated, suggesting the presence of temporal markers. The study highlights the potential of machine learning models like OpenCLIP in dating images and emphasizes the importance of fine-tuning for accurate temporal analysis. Future research should explore the application of these findings to color photographs and diverse datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge