Better Language Models with Model Merging
Paper and Code
Apr 17, 1996


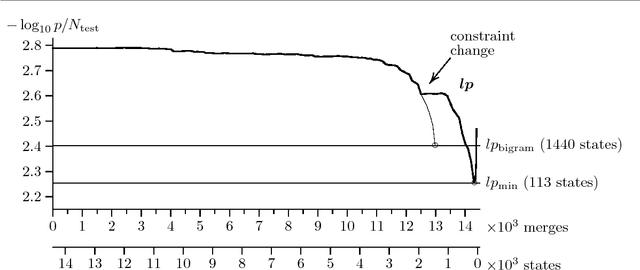
This paper investigates model merging, a technique for deriving Markov models from text or speech corpora. Models are derived by starting with a large and specific model and by successively combining states to build smaller and more general models. We present methods to reduce the time complexity of the algorithm and report on experiments on deriving language models for a speech recognition task. The experiments show the advantage of model merging over the standard bigram approach. The merged model assigns a lower perplexity to the test set and uses considerably fewer states.
* LaTeX, 9 pages. In Proceedings of EMNLP-96, Philadelphia, PA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge