Benchmarking Defeasible Reasoning with Large Language Models -- Initial Experiments and Future Directions
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2024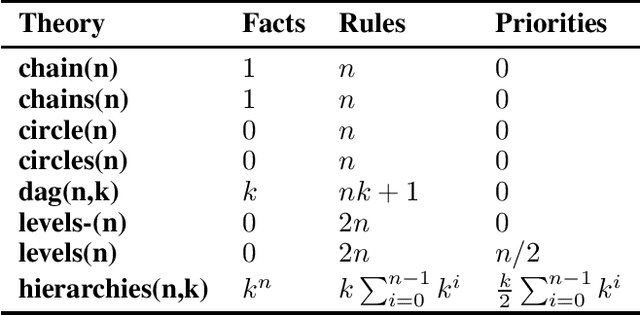
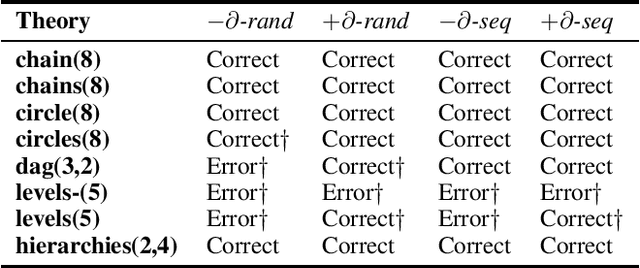
Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained prominence in the AI landscape due to their exceptional performance. Thus, it is essential to gain a better understanding of their capabilities and limitations, among others in terms of nonmonotonic reasoning. This paper proposes a benchmark that corresponds to various defeasible rule-based reasoning patterns. We modified an existing benchmark for defeasible logic reasoners by translating defeasible rules into text suitable for LLMs. We conducted preliminary experiments on nonmonotonic rule-based reasoning using ChatGPT and compared it with reasoning patterns defined by defeasible logic.
* Presented at NeLaMKRR@KR, 2024 (arXiv:2410.05339)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge