Bayesian inference of a new Mallows model for characterising symptom sequences applied in primary progressive aphasia
Paper and Code
Nov 22, 2023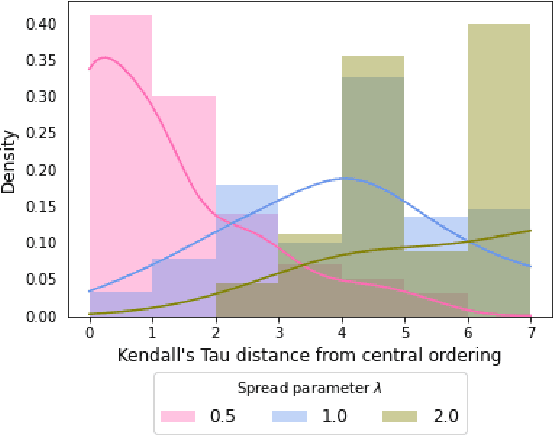
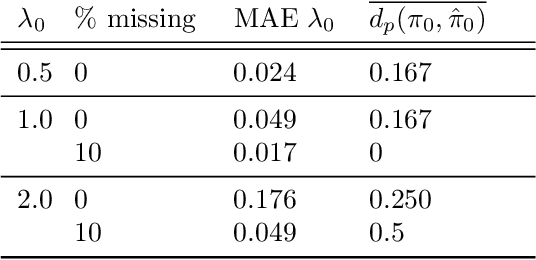
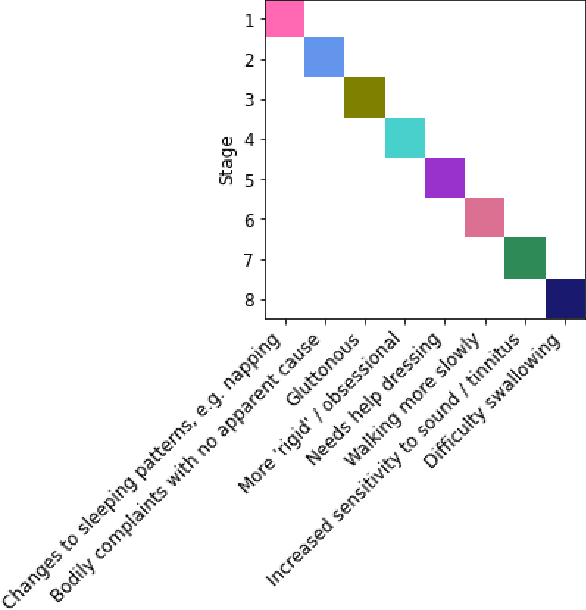
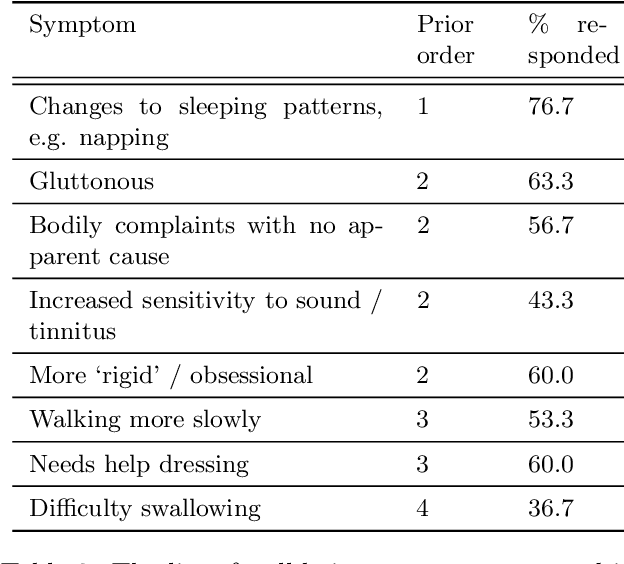
Machine learning models offer the potential to understand diverse datasets in a data-driven way, powering insights into individual disease experiences and ensuring equitable healthcare. In this study, we explore Bayesian inference for characterising symptom sequences, and the associated modelling challenges. We adapted the Mallows model to account for partial rankings and right-censored data, employing custom MCMC fitting. Our evaluation, encompassing synthetic data and a primary progressive aphasia dataset, highlights the model's efficacy in revealing mean orderings and estimating ranking variance. This holds the potential to enhance clinical comprehension of symptom occurrence. However, our work encounters limitations concerning model scalability and small dataset sizes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge