Automatic identification of outliers in Hubble Space Telescope galaxy images
Paper and Code
Jan 07, 2021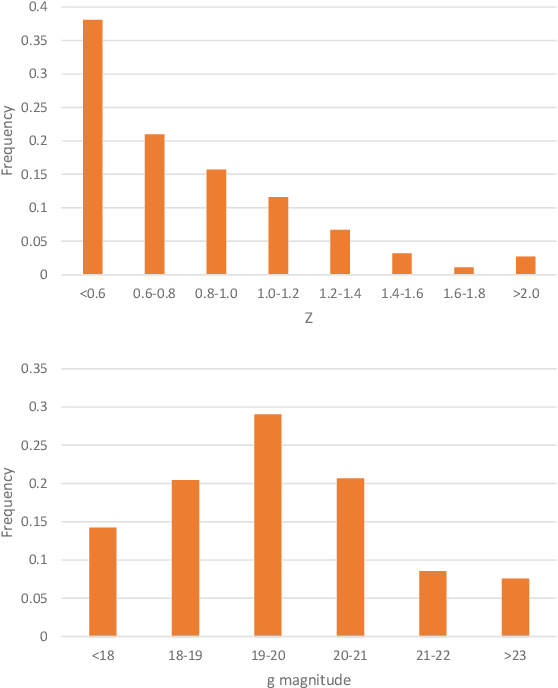
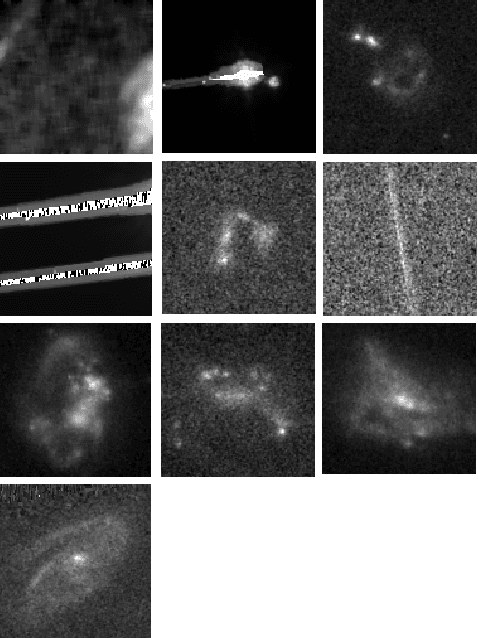
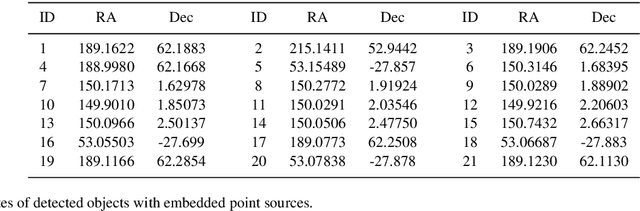

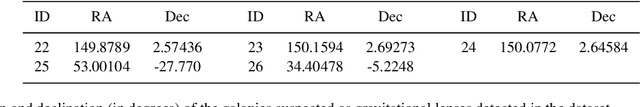
Rare extragalactic objects can carry substantial information about the past, present, and future universe. Given the size of astronomical databases in the information era it can be assumed that very many outlier galaxies are included in existing and future astronomical databases. However, manual search for these objects is impractical due to the required labor, and therefore the ability to detect such objects largely depends on computer algorithms. This paper describes an unsupervised machine learning algorithm for automatic detection of outlier galaxy images, and its application to several Hubble Space Telescope fields. The algorithm does not require training, and therefore is not dependent on the preparation of clean training sets. The application of the algorithm to a large collection of galaxies detected a variety of outlier galaxy images. The algorithm is not perfect in the sense that not all objects detected by the algorithm are indeed considered outliers, but it reduces the dataset by two orders of magnitude to allow practical manual identification. The catalogue contains 147 objects that would be very difficult to identify without using automation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge