Autoencoding Pixies: Amortised Variational Inference with Graph Convolutions for Functional Distributional Semantics
Paper and Code
May 10, 2020
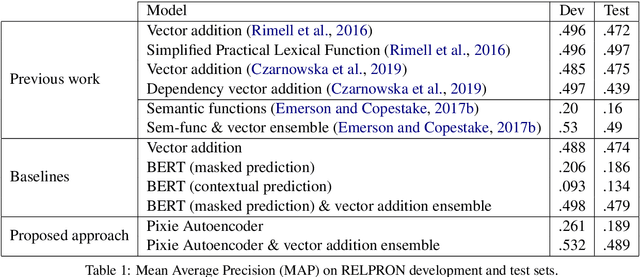
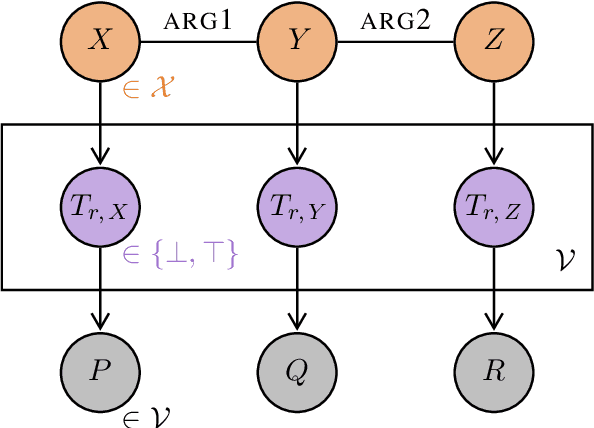

Functional Distributional Semantics provides a linguistically interpretable framework for distributional semantics, by representing the meaning of a word as a function (a binary classifier), instead of a vector. However, the large number of latent variables means that inference is computationally expensive, and training a model is therefore slow to converge. In this paper, I introduce the Pixie Autoencoder, which augments the generative model of Functional Distributional Semantics with a graph-convolutional neural network to perform amortised variational inference. This allows the model to be trained more effectively, achieving better results on two tasks (semantic similarity in context and semantic composition), and outperforming BERT, a large pre-trained language model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge