Audiovisual angle and voice incongruence do not affect audiovisual verbal short-term memory in virtual reality
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2024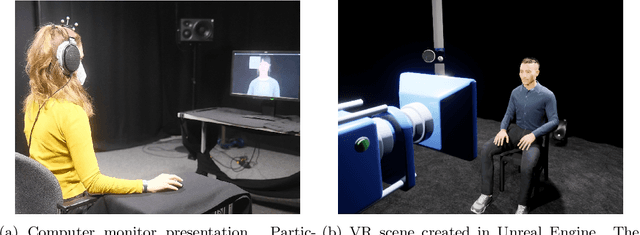
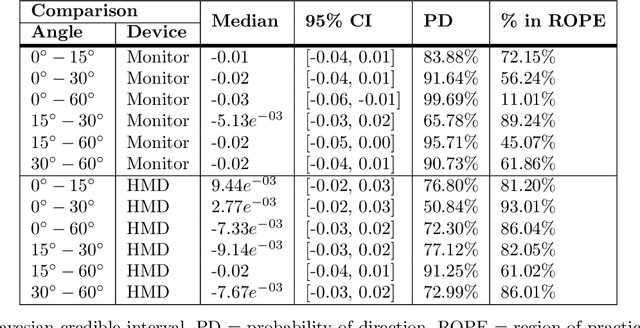
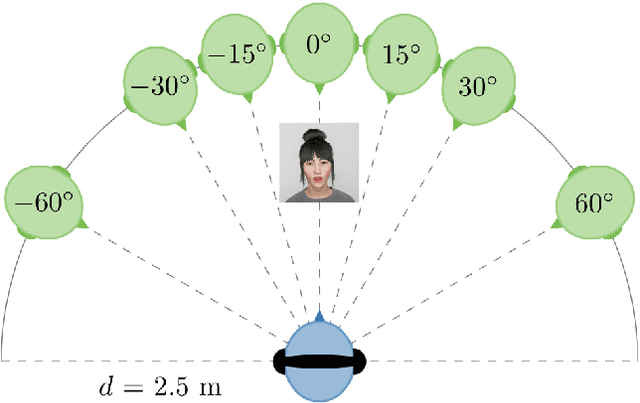
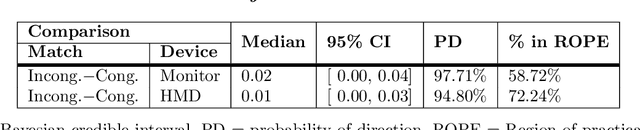
Virtual reality (VR) environments are frequently used in auditory and cognitive research to imitate real-life scenarios, presumably enhancing state-of-the-art approaches with traditional computer screens. However, the effects of different display technologies on audiovisual processing remain underexplored. This study investigated how VR displayed with an head-mounted display (HMD) affects serial recall performance compared to traditional computer monitors, focusing on their effects on audiovisual processing in cognitive tasks. For that matter, we conducted two experiments with both an HMD and a computer monitor as display devices and two types of audiovisual incongruences: angle (Exp. 1) and voice (Exp. 2) incongruence. To quantify cognitive performance an audiovisual verbal serial recall (avVSR) task was developed where an embodied conversational agent (ECA) was animated to speak the target digit sequence. Even though subjective evaluations showed a higher sense of presence in the HMD condition, we found no effect of the display device on the proportion of correctly recalled digits. For the extreme conditions of angle incongruence in the computer monitor presentation the proportion of correctly recalled digits increased marginally, presumably due to raised attention, but the effect is likely too small to be meaningful. Response times were not affected by incongruences in either display device across both experiments. These findings suggest that the avVSR task is robust against angular and voice audiovisual incongruences, irrespective of the display device, at least for the conditions studied here. Hence, the study introduces the avVSR task in VR and contributes to the understanding of audiovisual integration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge