AResNet-ViT: A Hybrid CNN-Transformer Network for Benign and Malignant Breast Nodule Classification in Ultrasound Images
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2024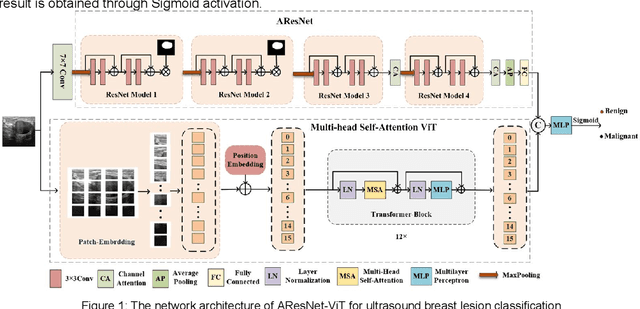
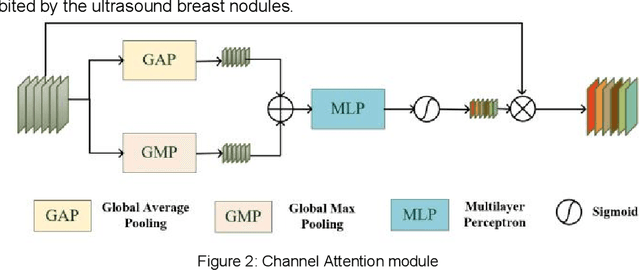
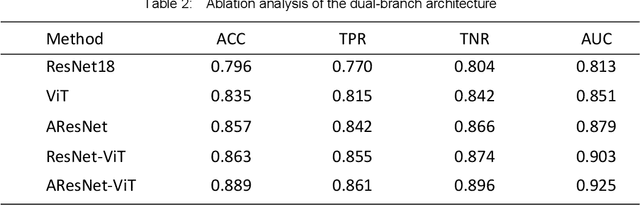
To address the challenges of similarity between lesions and surrounding tissues, overlapping appearances of partially benign and malignant nodules, and difficulty in classification, a deep learning network that integrates CNN and Transformer is proposed for the classification of benign and malignant breast lesions in ultrasound images. This network adopts a dual-branch architecture for local-global feature extraction, making full use of the advantages of CNN in extracting local features and the ability of ViT to extract global features to enhance the network's feature extraction capabilities for breast nodules. The local feature extraction branch employs a residual network with multiple attention-guided modules, which can effectively capture the local details and texture features of breast nodules, enhance sensitivity to subtle changes within the nodules, and thus can aid in accurate classification of their benign and malignancy. The global feature extraction branch utilizes the multi-head self-attention ViT network, which can capture the overall shape, boundary, and relationship with surrounding tissues, and thereby enhancing the understanding and modeling of both nodule and global image features. Experimental results on a public ultrasound breast nodule data set show that the proposed method is better than other comparison networks, This indicates that the fusion of CNN and Transformer networks can effectively improve the performance of the classification model and provide a powerful solution for the benign-malignant classification of ultrasound breast.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge