Analyzing the Variations in Emergency Department Boarding and Testing the Transferability of Forecasting Models across COVID-19 Pandemic Waves in Hong Kong: Hybrid CNN-LSTM approach to quantifying building-level socioecological risk
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2024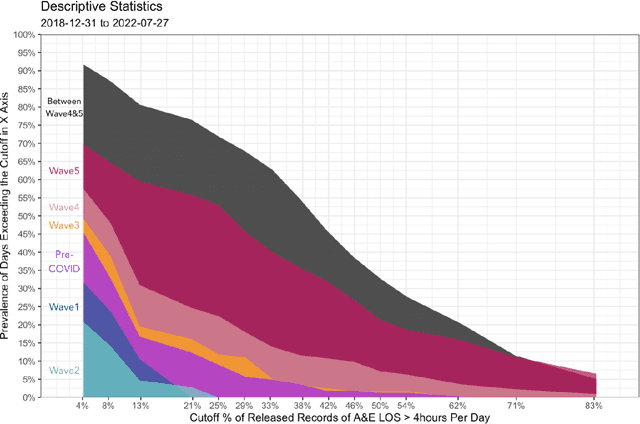
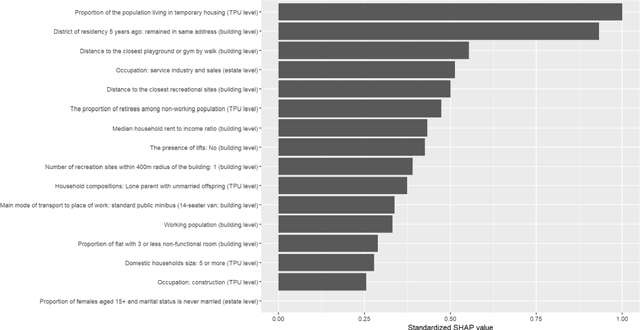
Emergency department's (ED) boarding (defined as ED waiting time greater than four hours) has been linked to poor patient outcomes and health system performance. Yet, effective forecasting models is rare before COVID-19, lacking during the peri-COVID era. Here, a hybrid convolutional neural network (CNN)-Long short-term memory (LSTM) model was applied to public-domain data sourced from Hong Kong's Hospital Authority, Department of Health, and Housing Authority. In addition, we sought to identify the phase of the COVID-19 pandemic that most significantly perturbed our complex adaptive healthcare system, thereby revealing a stable pattern of interconnectedness among its components, using deep transfer learning methodology. Our result shows that 1) the greatest proportion of days with ED boarding was found between waves four and five; 2) the best-performing model for forecasting ED boarding was observed between waves four and five, which was based on features representing time-invariant residential buildings' built environment and sociodemographic profiles and the historical time series of ED boarding and case counts, compared to during the waves when best-performing forecasting is based on time-series features alone; and 3) when the model built from the period between waves four and five was applied to data from other waves via deep transfer learning, the transferred model enhanced the performance of indigenous models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge