Analysis Co-Sparse Coding for Energy Disaggregation
Paper and Code
Dec 11, 2019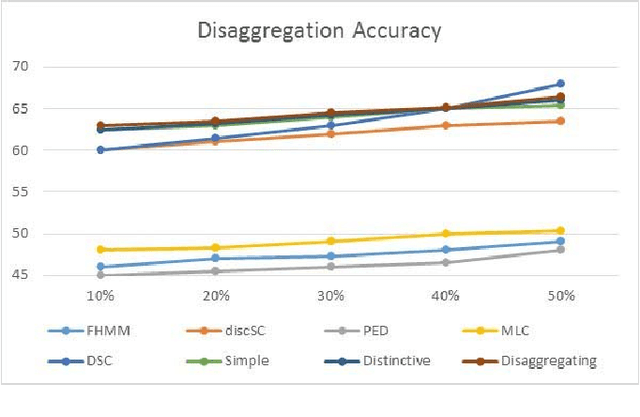
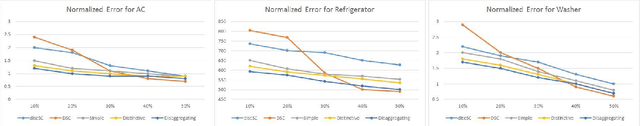
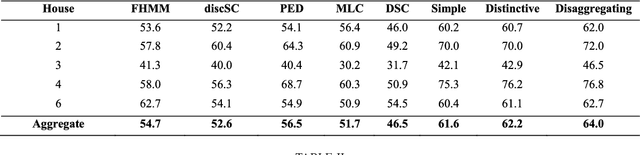
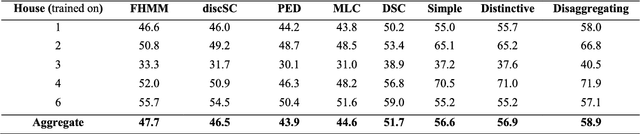
Energy disaggregation is the task of segregating the aggregate energy of the entire building (as logged by the smartmeter) into the energy consumed by individual appliances. This is a single channel (the only channel being the smart-meter) blind source (different electrical appliances) separation problem. In recent times dictionary learning based approaches have shown promise in addressing the disaggregation problem. The usual technique is to learn a dictionary for every device and use the learnt dictionaries as basis for blind source separation during disaggregation. Dictionary learning is a synthesis formulation; in this work, we propose an analysis approach. The advantage of our proposed approach is that, the requirement of training volume drastically reduces compared to state-of-the-art techniques. This means that, we require fewer instrumented homes, or fewer days of instrumentation per home; in either case this drastically reduces the sensing cost. Results on two benchmark datasets show that our method produces the same level of disaggregation accuracy as state-of-the-art methods but with only a fraction of the training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge