Analog CMOS-based Resistive Processing Unit for Deep Neural Network Training
Paper and Code
Jun 20, 2017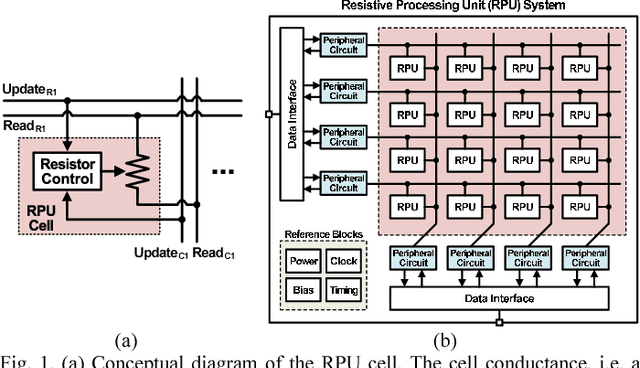
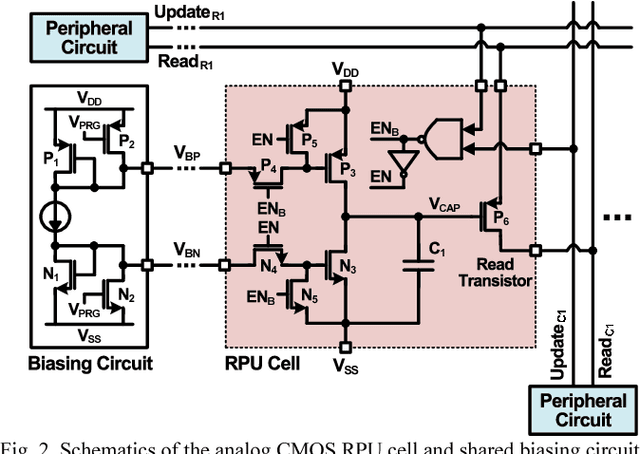
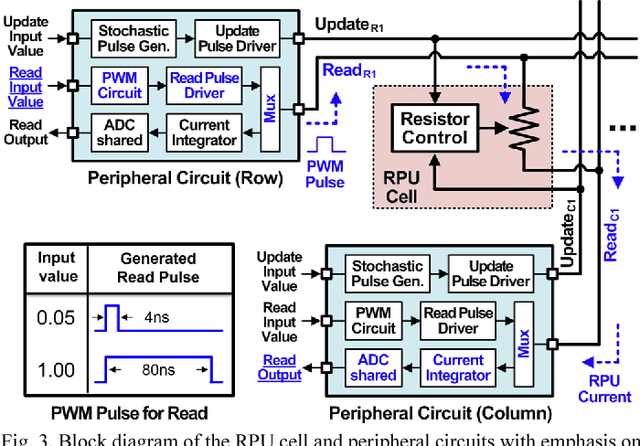
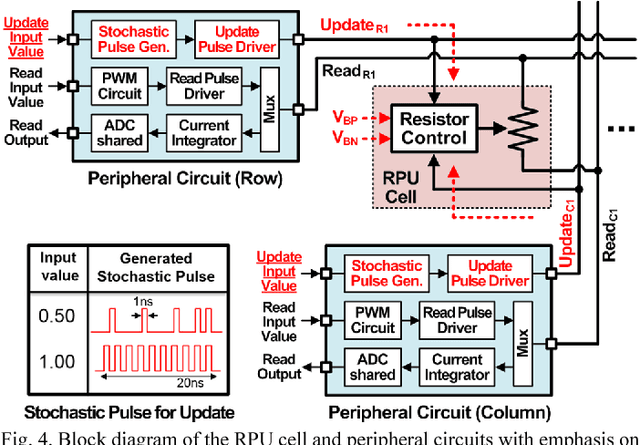
Recently we have shown that an architecture based on resistive processing unit (RPU) devices has potential to achieve significant acceleration in deep neural network (DNN) training compared to today's software-based DNN implementations running on CPU/GPU. However, currently available device candidates based on non-volatile memory technologies do not satisfy all the requirements to realize the RPU concept. Here, we propose an analog CMOS-based RPU design (CMOS RPU) which can store and process data locally and can be operated in a massively parallel manner. We analyze various properties of the CMOS RPU to evaluate the functionality and feasibility for acceleration of DNN training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge