An unsupervised bayesian approach for the joint reconstruction and classification of cutaneous reflectance confocal microscopy images
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2017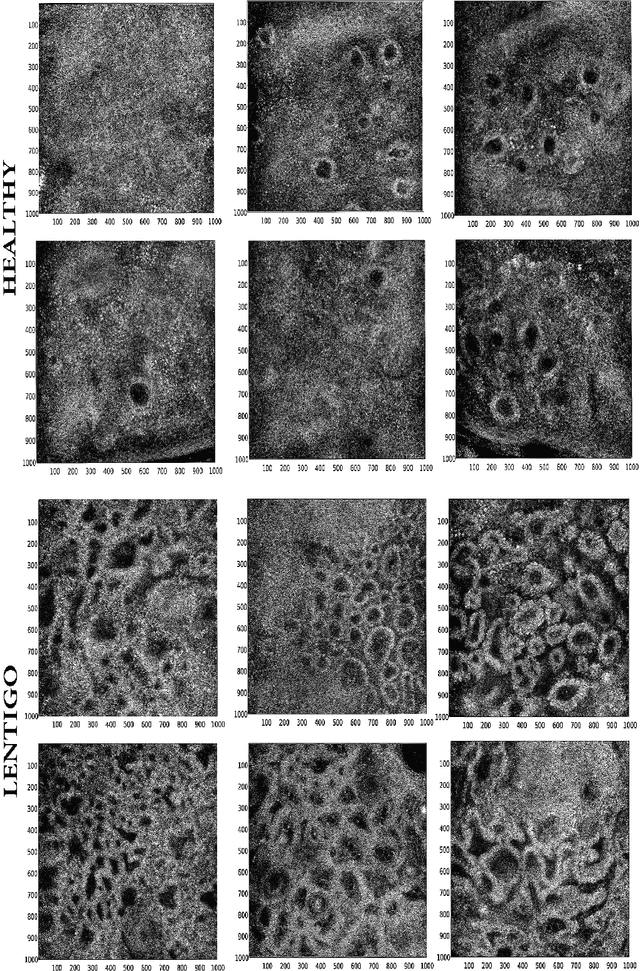
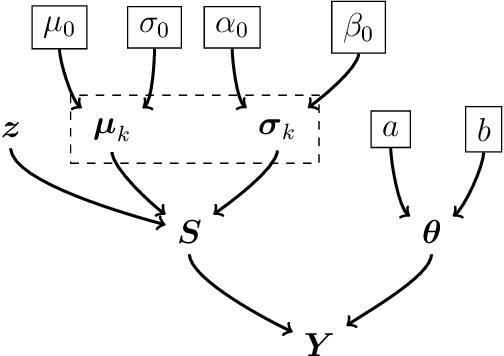
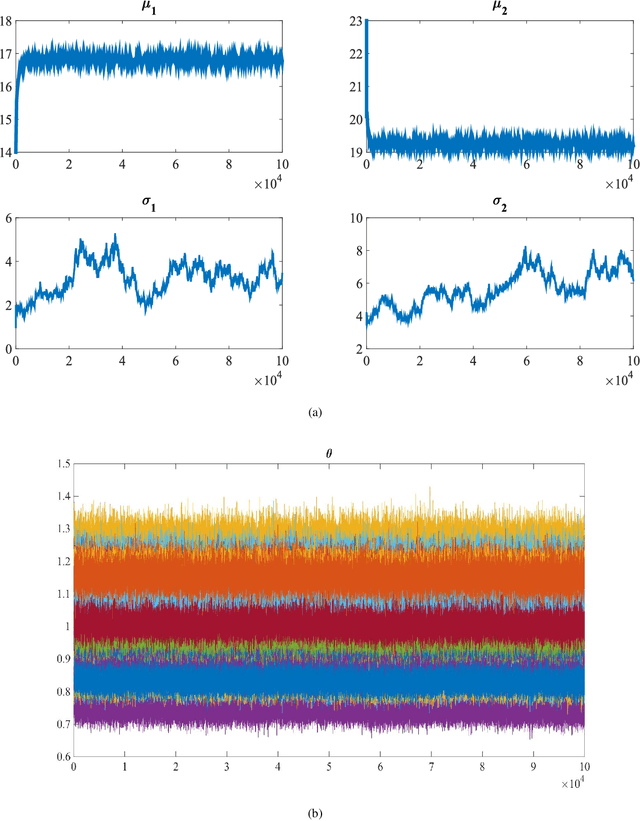
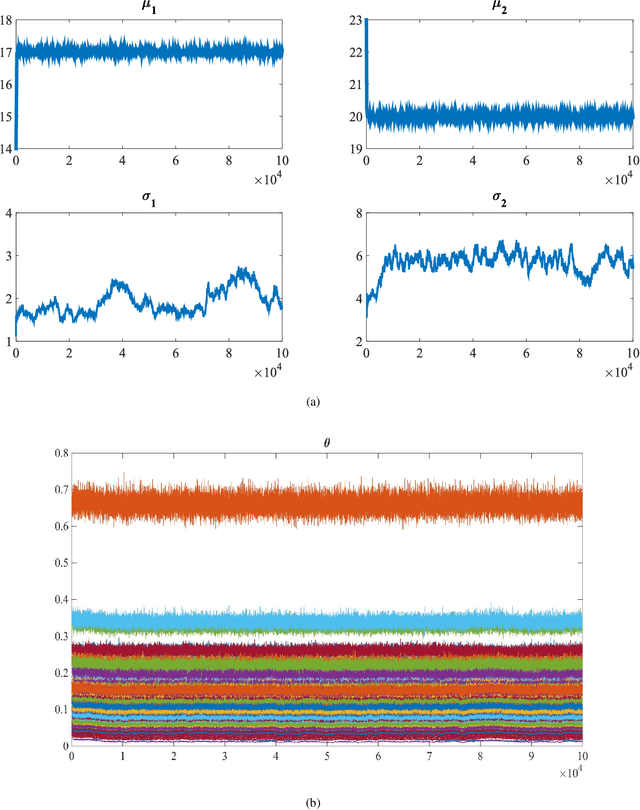
This paper studies a new Bayesian algorithm for the joint reconstruction and classification of reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) images, with application to the identification of human skin lentigo. The proposed Bayesian approach takes advantage of the distribution of the multiplicative speckle noise affecting the true reflectivity of these images and of appropriate priors for the unknown model parameters. A Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm is proposed to jointly estimate the model parameters and the image of true reflectivity while classifying images according to the distribution of their reflectivity. Precisely, a Metropolis-whitin-Gibbs sampler is investigated to sample the posterior distribution of the Bayesian model associated with RCM images and to build estimators of its parameters, including labels indicating the class of each RCM image. The resulting algorithm is applied to synthetic data and to real images from a clinical study containing healthy and lentigo patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge