An Information Diffusion Approach to Rumor Propagation and Identification on Twitter
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2020
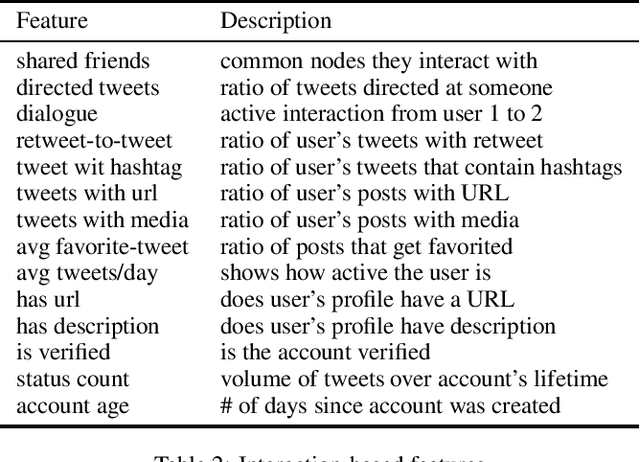
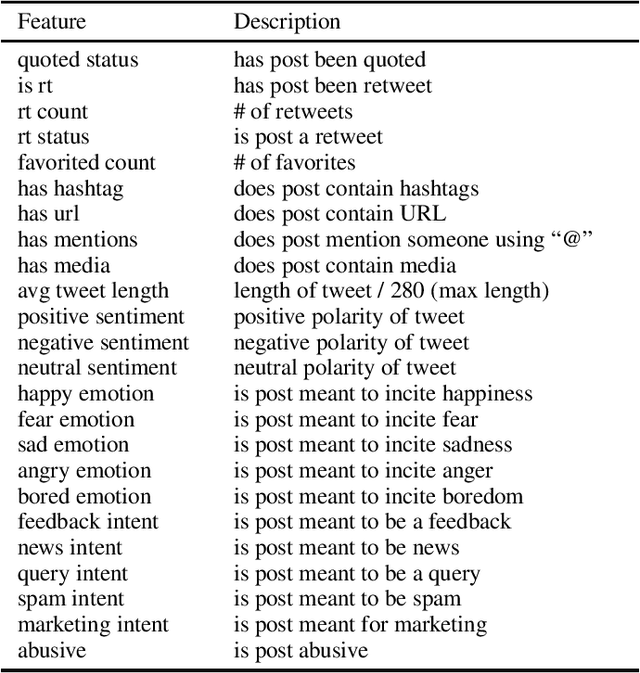
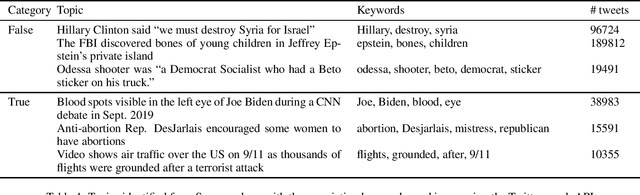
With the increasing use of online social networks as a source of news and information, the propensity for a rumor to disseminate widely and quickly poses a great concern, especially in disaster situations where users do not have enough time to fact-check posts before making the informed decision to react to a post that appears to be credible. In this study, we explore the propagation pattern of rumors on Twitter by exploring the dynamics of microscopic-level misinformation spread, based on the latent message and user interaction attributes. We perform supervised learning for feature selection and prediction. Experimental results with real-world data sets give the models' prediction accuracy at about 90\% for the diffusion of both True and False topics. Our findings confirm that rumor cascades run deeper and that rumor masked as news, and messages that incite fear, will diffuse faster than other messages. We show that the models for True and False message propagation differ significantly, both in the prediction parameters and in the message features that govern the diffusion. Finally, we show that the diffusion pattern is an important metric in identifying the credibility of a tweet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge