An inertial forward-backward algorithm for monotone inclusions
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2014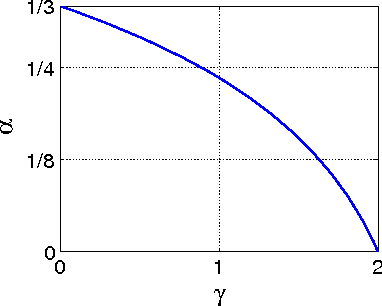
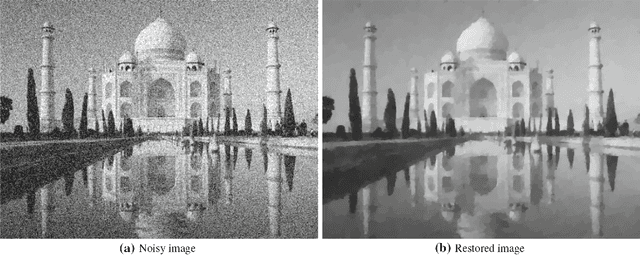
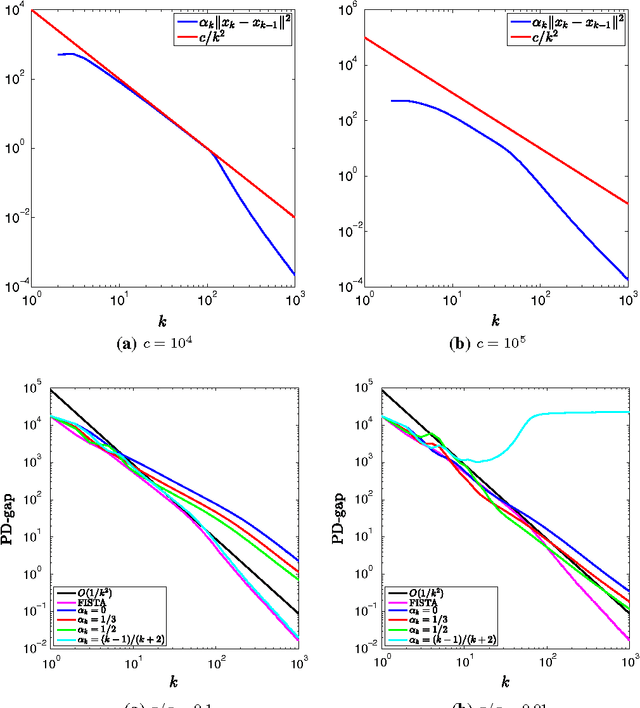
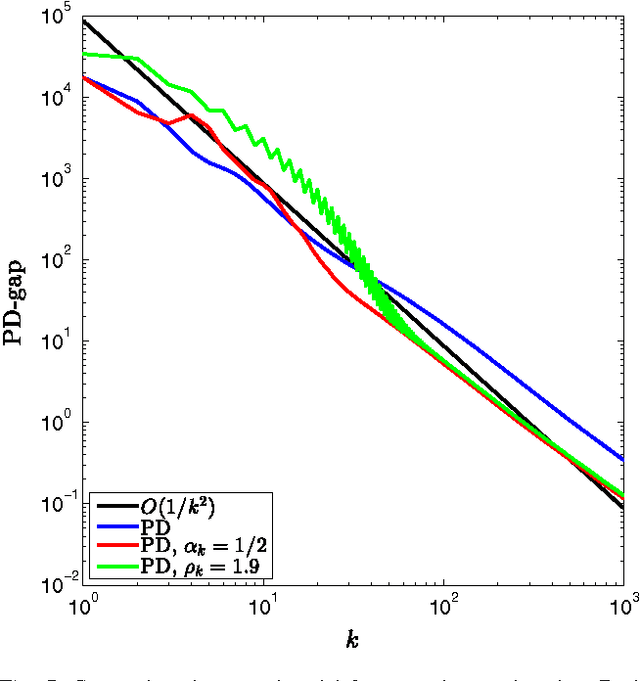
In this paper, we propose an inertial forward backward splitting algorithm to compute a zero of the sum of two monotone operators, with one of the two operators being co-coercive. The algorithm is inspired by the accelerated gradient method of Nesterov, but can be applied to a much larger class of problems including convex-concave saddle point problems and general monotone inclusions. We prove convergence of the algorithm in a Hilbert space setting and show that several recently proposed first-order methods can be obtained as special cases of the general algorithm. Numerical results show that the proposed algorithm converges faster than existing methods, while keeping the computational cost of each iteration basically unchanged.
* The final publication is available at http://link.springer.com
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge