An empirical study on speech restoration guided by self supervised speech representation
Paper and Code
May 30, 2023
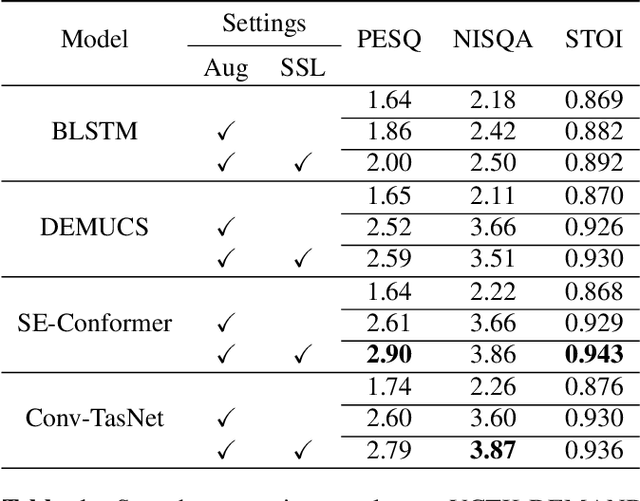


Enhancing speech quality is an indispensable yet difficult task as it is often complicated by a range of degradation factors. In addition to additive noise, reverberation, clipping, and speech attenuation can all adversely affect speech quality. Speech restoration aims to recover speech components from these distortions. This paper focuses on exploring the impact of self-supervised speech representation learning on the speech restoration task. Specifically, we employ speech representation in various speech restoration networks and evaluate their performance under complicated distortion scenarios. Our experiments demonstrate that the contextual information provided by the self-supervised speech representation can enhance speech restoration performance in various distortion scenarios, while also increasing robustness against the duration of speech attenuation and mismatched test conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge