An Efficient Forecasting Approach to Reduce Boundary Effects in Real-Time Time-Frequency Analysis
Paper and Code
Feb 22, 2021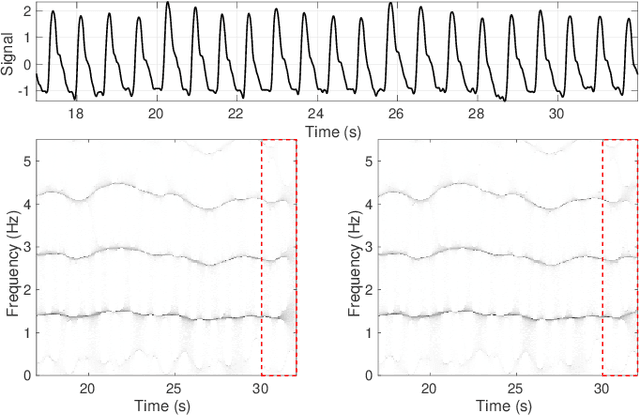
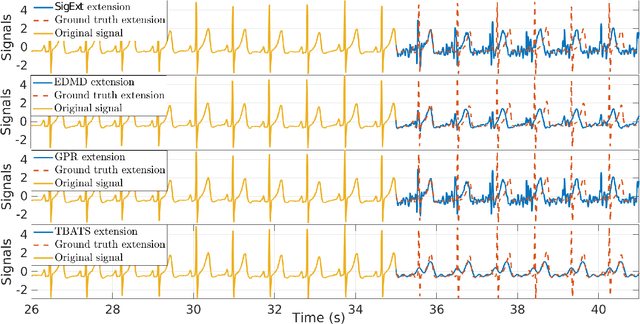
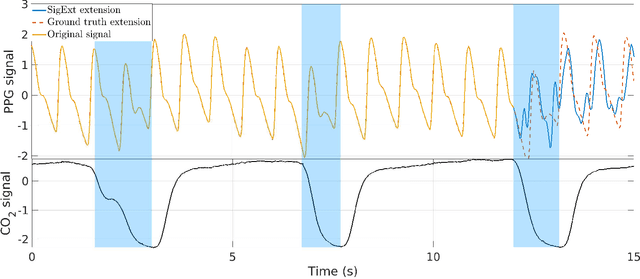
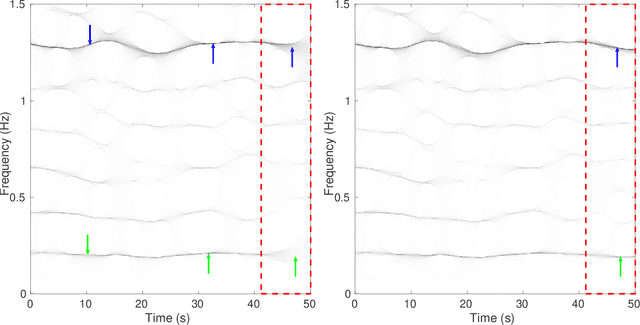
Time-frequency (TF) representations of time series are intrinsically subject to the boundary effects. As a result, the structures of signals that are highlighted by the representations are garbled when approaching the boundaries of the TF domain. In this paper, for the purpose of real-time TF information acquisition of nonstationary oscillatory time series, we propose a numerically efficient approach for the reduction of such boundary effects. The solution relies on an extension of the analyzed signal obtained by a forecasting technique. In the case of the study of a class of locally oscillating signals, we provide a theoretical guarantee of the performance of our approach. Following a numerical verification of the algorithmic performance of our approach, we validate it by implementing it on biomedical signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge