An Audio Synthesis Framework Derived from Industrial Process Control
Paper and Code
Sep 21, 2021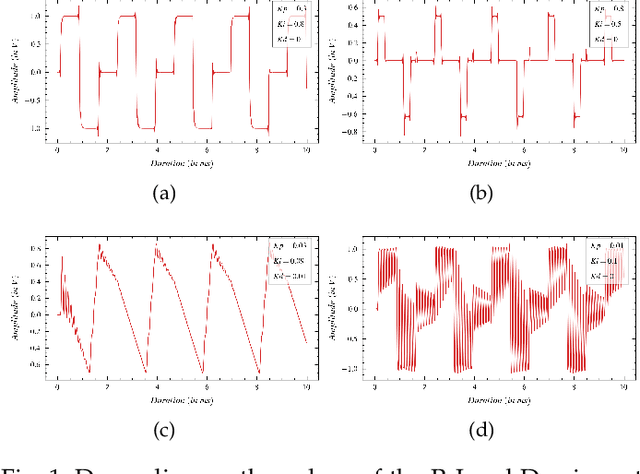



Since its conception, digital synthesis has significantly influenced the advancement of music, leading to new genres and production styles. Through existing synthesis techniques, one can recreate naturally occurring sounds as well as generate innovative artificial timbres. However, research in audio technology continues to pursue new methods of synthesizing sounds, keeping the transformation of music constant. This research attempts to formulate the framework of a new synthesis technique by redefining the popular Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) algorithm used in feedback-based process control. The framework is then implemented as a Python application to study the available control parameters and their effect on the synthesized output. Further, applications of this technique as an audio signal and LFO generator, including its potentiality as an alternative to FM and Wavetable synthesis techniques, are studied in detail. The research concludes by highlighting some of the imperfections in the current framework and the possible research directions to be considered to address them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge