AI Gone Astray: Technical Supplement
Paper and Code
Mar 01, 2022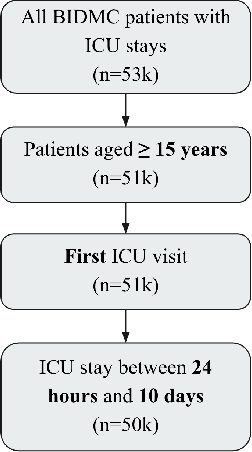
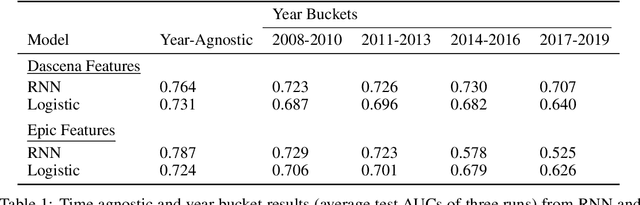
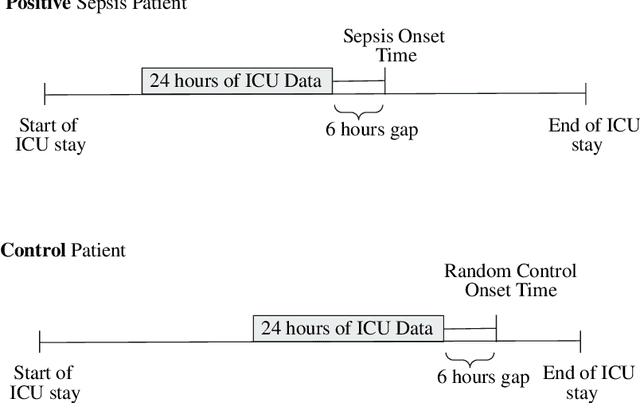
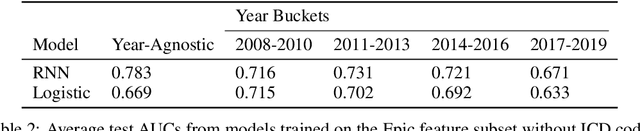
This study is a technical supplement to "AI gone astray: How subtle shifts in patient data send popular algorithms reeling, undermining patient safety." from STAT News, which investigates the effect of time drift on clinically deployed machine learning models. We use MIMIC-IV, a publicly available dataset, to train models that replicate commercial approaches by Dascena and Epic to predict the onset of sepsis, a deadly and yet treatable condition. We observe some of these models degrade overtime; most notably an RNN built on Epic features degrades from a 0.729 AUC to a 0.525 AUC over a decade, leading us to investigate technical and clinical drift as root causes of this performance drop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge