Adversarial NLI for Factual Correctness in Text Summarisation Models
Paper and Code
May 24, 2020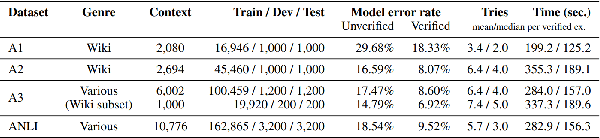
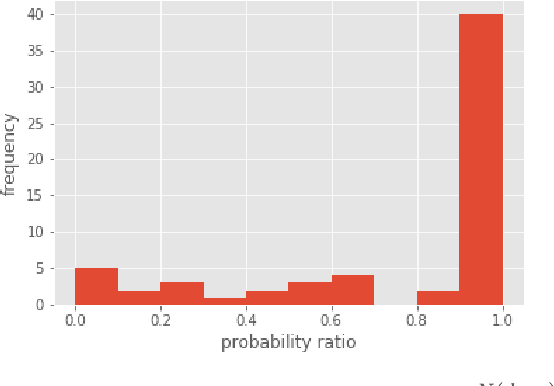

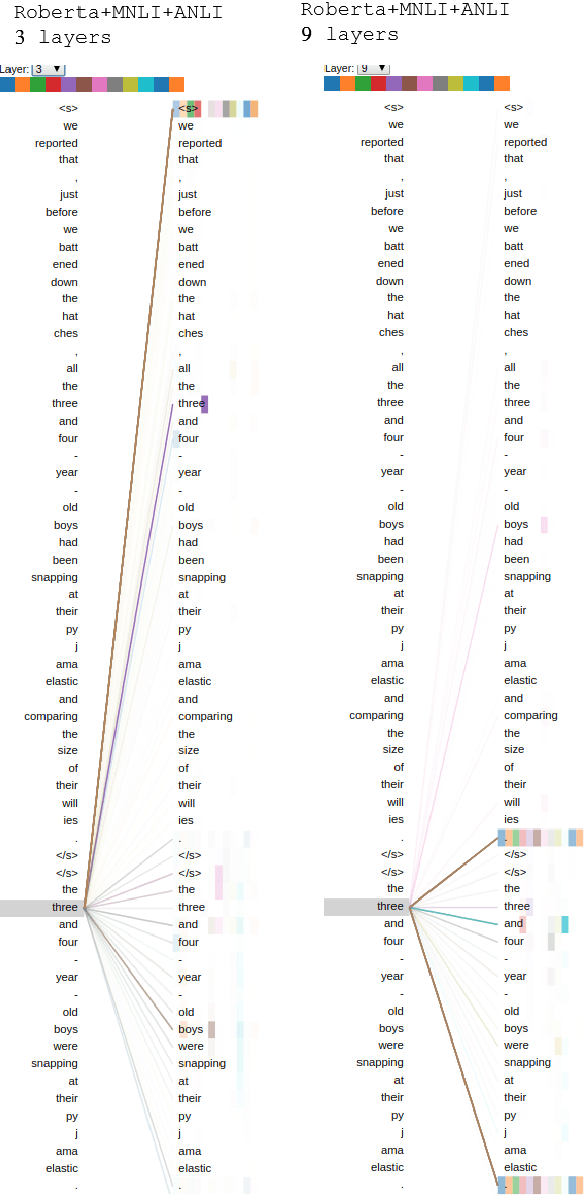
We apply the Adversarial NLI dataset to train the NLI model and show that the model has the potential to enhance factual correctness in abstract summarization. We follow the work of Falke et al. (2019), which rank multiple generated summaries based on the entailment probabilities between an source document and summaries and select the summary that has the highest entailment probability. The authors' earlier study concluded that current NLI models are not sufficiently accurate for the ranking task. We show that the Transformer models fine-tuned on the new dataset achieve significantly higher accuracy and have the potential of selecting a coherent summary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge