Adversarial Defense of Image Classification Using a Variational Auto-Encoder
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2018
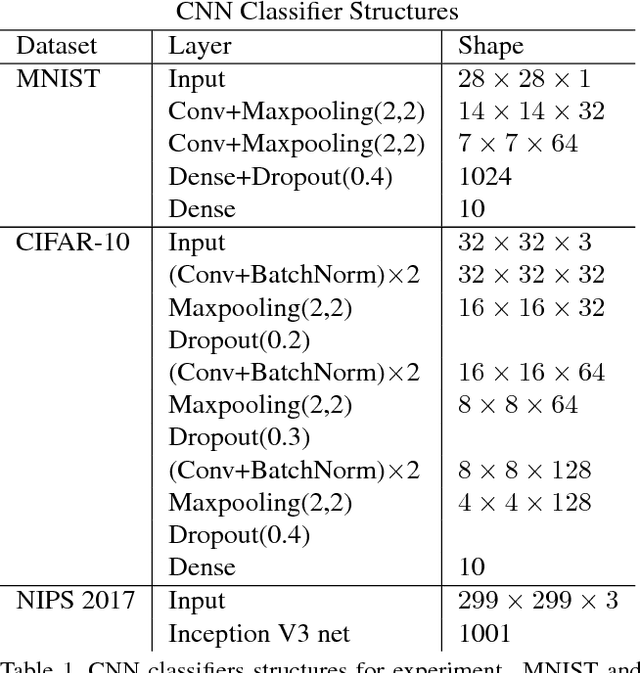
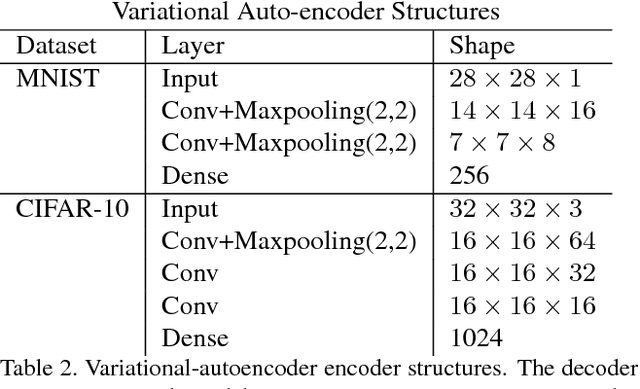

Deep neural networks are known to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks. This exposes them to potential exploits in security-sensitive applications and highlights their lack of robustness. This paper uses a variational auto-encoder (VAE) to defend against adversarial attacks for image classification tasks. This VAE defense has a few nice properties: (1) it is quite flexible and its use of randomness makes it harder to attack; (2) it can learn disentangled representations that prevent blurry reconstruction; and (3) a patch-wise VAE defense strategy is used that does not require retraining for different size images. For moderate to severe attacks, this system outperforms or closely matches the performance of JPEG compression, with the best quality parameter. It also has more flexibility and potential for improvement via training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge