Adaptive Voronoi NeRFs
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2023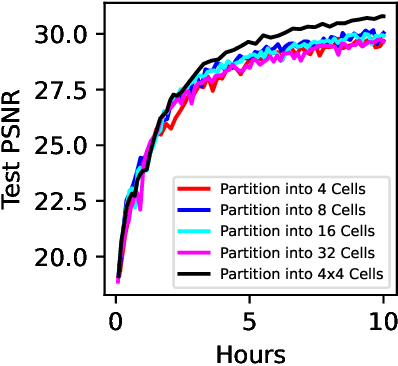
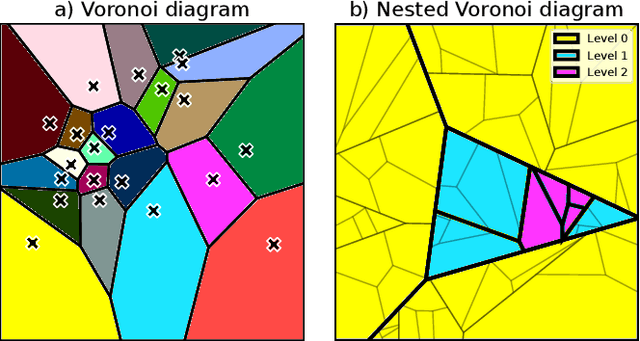
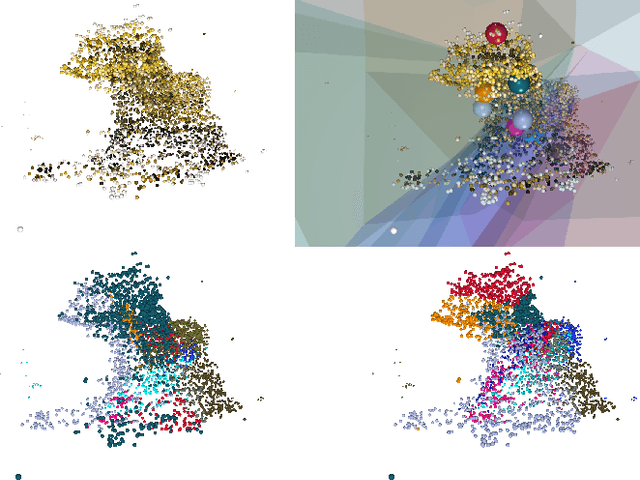
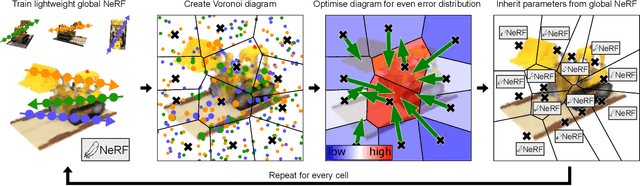
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) learn to represent a 3D scene from just a set of registered images. Increasing sizes of a scene demands more complex functions, typically represented by neural networks, to capture all details. Training and inference then involves querying the neural network millions of times per image, which becomes impractically slow. Since such complex functions can be replaced by multiple simpler functions to improve speed, we show that a hierarchy of Voronoi diagrams is a suitable choice to partition the scene. By equipping each Voronoi cell with its own NeRF, our approach is able to quickly learn a scene representation. We propose an intuitive partitioning of the space that increases quality gains during training by distributing information evenly among the networks and avoids artifacts through a top-down adaptive refinement. Our framework is agnostic to the underlying NeRF method and easy to implement, which allows it to be applied to various NeRF variants for improved learning and rendering speeds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge