ActiveHARNet: Towards On-Device Deep Bayesian Active Learning for Human Activity Recognition
Paper and Code
May 31, 2019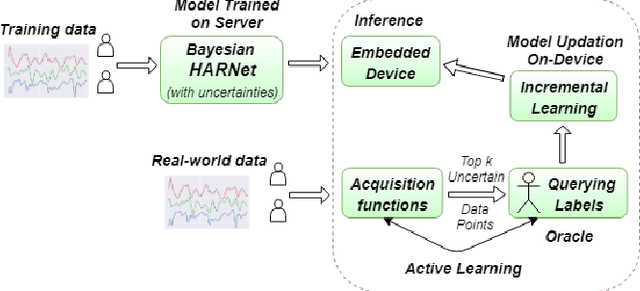
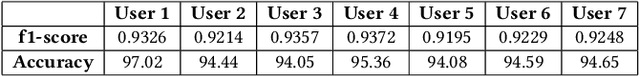
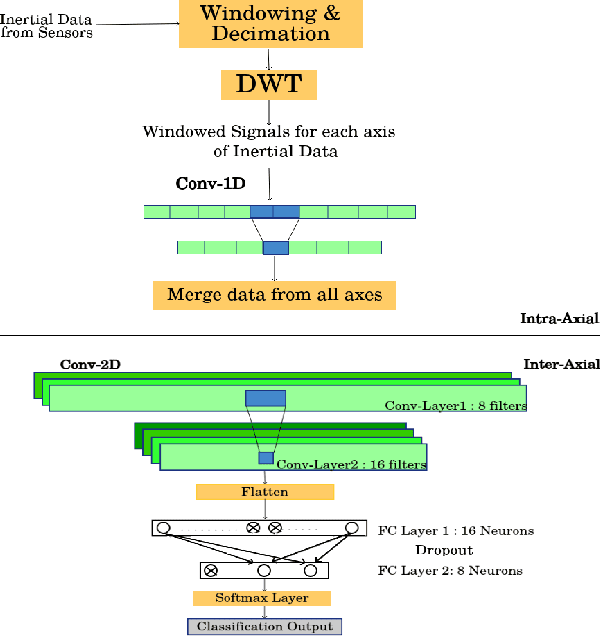
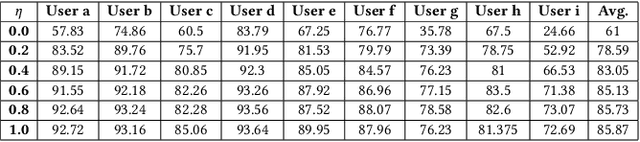
Various health-care applications such as assisted living, fall detection etc., require modeling of user behavior through Human Activity Recognition (HAR). HAR using mobile- and wearable-based deep learning algorithms have been on the rise owing to the advancements in pervasive computing. However, there are two other challenges that need to be addressed: first, the deep learning model should support on-device incremental training (model updation) from real-time incoming data points to learn user behavior over time, while also being resource-friendly; second, a suitable ground truthing technique (like Active Learning) should help establish labels on-the-fly while also selecting only the most informative data points to query from an oracle. Hence, in this paper, we propose ActiveHARNet, a resource-efficient deep ensembled model which supports on-device Incremental Learning and inference, with capabilities to represent model uncertainties through approximations in Bayesian Neural Networks using dropout. This is combined with suitable acquisition functions for active learning. Empirical results on two publicly available wrist-worn HAR and fall detection datasets indicate that ActiveHARNet achieves considerable efficiency boost during inference across different users, with a substantially low number of acquired pool points (at least 60% reduction) during incremental learning on both datasets experimented with various acquisition functions, thus demonstrating deployment and Incremental Learning feasibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge