A Study into the similarity in generator and discriminator in GAN architecture
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2018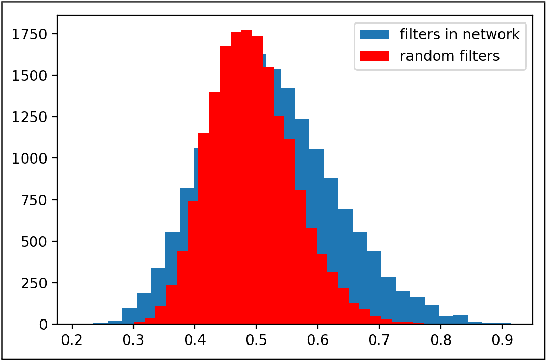
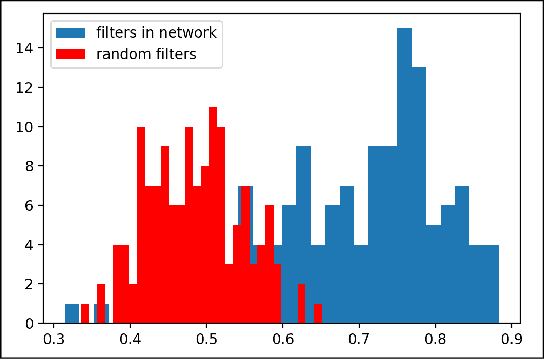
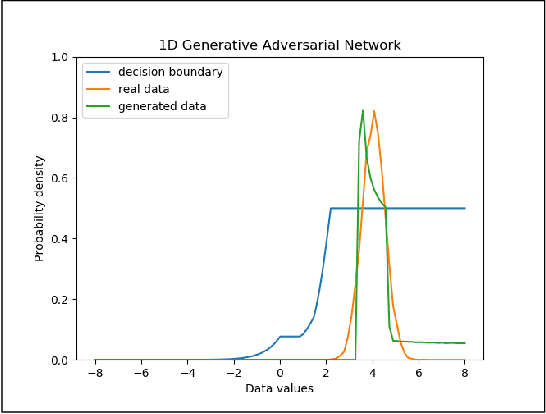
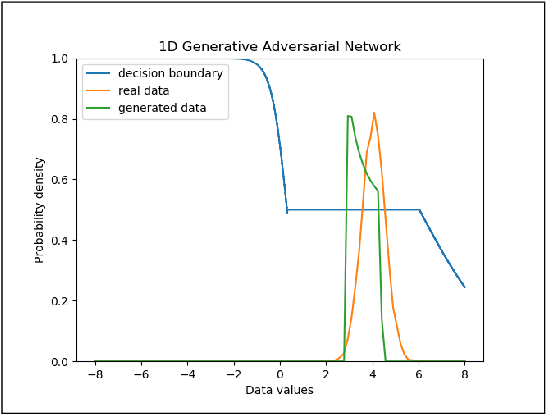
One popular generative model that has high-quality results is the Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN). This type of architecture consists of two separate networks that play against each other. The generator creates an output from the input noise that is given to it. The discriminator has the task of determining if the input to it is real or fake. This takes place constantly eventually leads to the generator modeling the target distribution. This paper includes a study into the actual weights learned by the network and a study into the similarity of the discriminator and generator networks. The paper also tries to leverage the similarity between these networks and shows that indeed both the networks may have a similar structure with experimental evidence with a novel shared architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge