A Restricted-Domain Dual Formulation for Two-Phase Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2018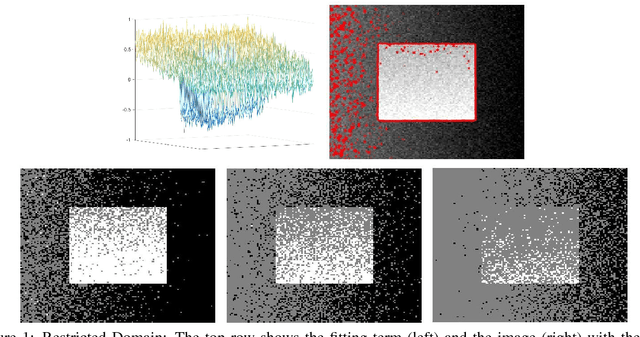
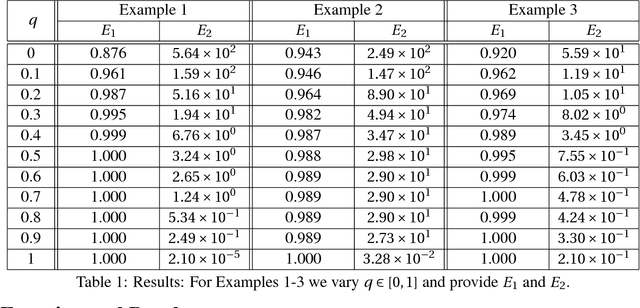
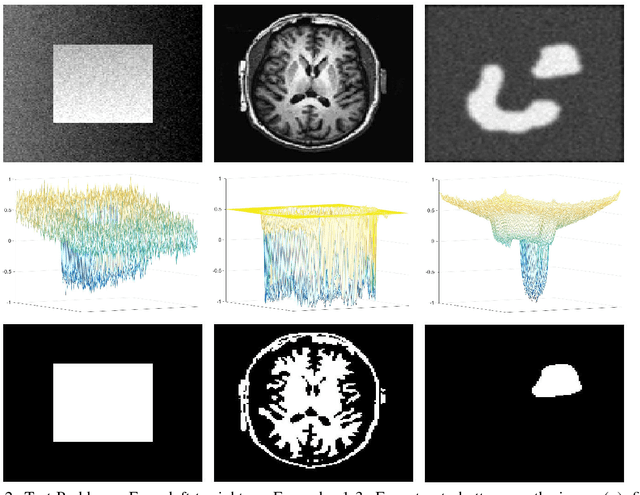
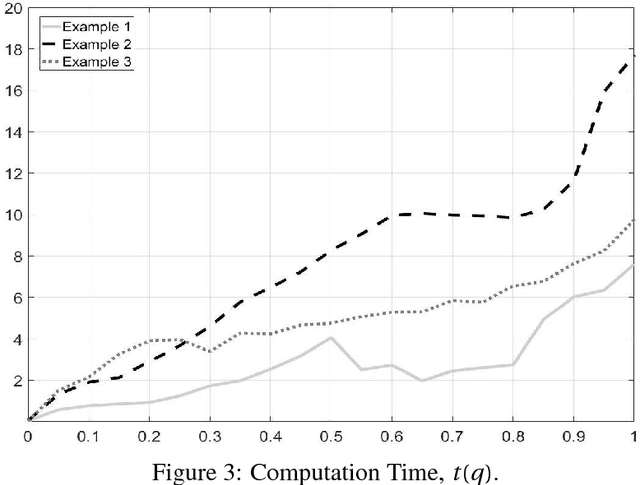
In two-phase image segmentation, convex relaxation has allowed global minimisers to be computed for a variety of data fitting terms. Many efficient approaches exist to compute a solution quickly. However, we consider whether the nature of the data fitting in this formulation allows for reasonable assumptions to be made about the solution that can improve the computational performance further. In particular, we employ a well known dual formulation of this problem and solve the corresponding equations in a restricted domain. We present experimental results that explore the dependence of the solution on this restriction and quantify imrovements in the computational performance. This approach can be extended to analogous methods simply and could provide an efficient alternative for problems of this type.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge