A Pointillism Approach for Natural Language Processing of Social Media
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2012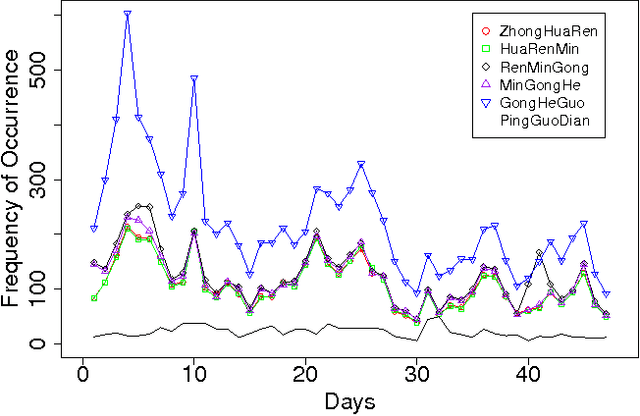

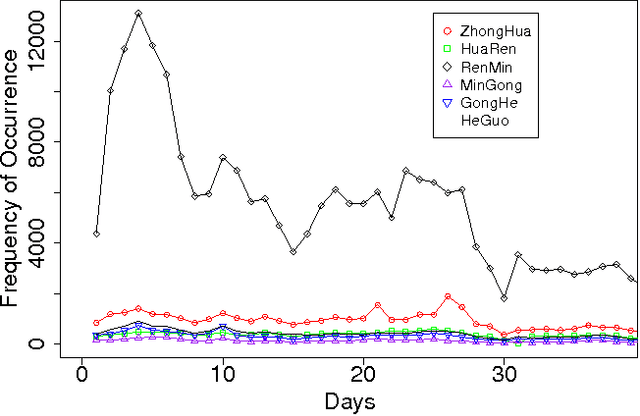
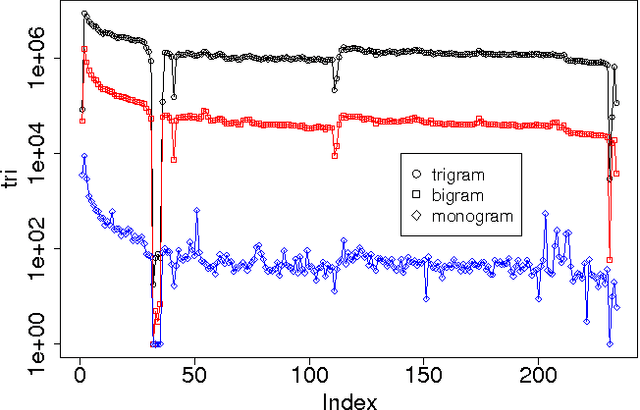
The Chinese language poses challenges for natural language processing based on the unit of a word even for formal uses of the Chinese language, social media only makes word segmentation in Chinese even more difficult. In this document we propose a pointillism approach to natural language processing. Rather than words that have individual meanings, the basic unit of a pointillism approach is trigrams of characters. These grams take on meaning in aggregate when they appear together in a way that is correlated over time. Our results from three kinds of experiments show that when words and topics do have a meme-like trend, they can be reconstructed from only trigrams. For example, for 4-character idioms that appear at least 99 times in one day in our data, the unconstrained precision (that is, precision that allows for deviation from a lexicon when the result is just as correct as the lexicon version of the word or phrase) is 0.93. For longer words and phrases collected from Wiktionary, including neologisms, the unconstrained precision is 0.87. We consider these results to be very promising, because they suggest that it is feasible for a machine to reconstruct complex idioms, phrases, and neologisms with good precision without any notion of words. Thus the colorful and baroque uses of language that typify social media in challenging languages such as Chinese may in fact be accessible to machines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge