A Novel Estimator of Mutual Information for Learning to Disentangle Textual Representations
Paper and Code
May 06, 2021
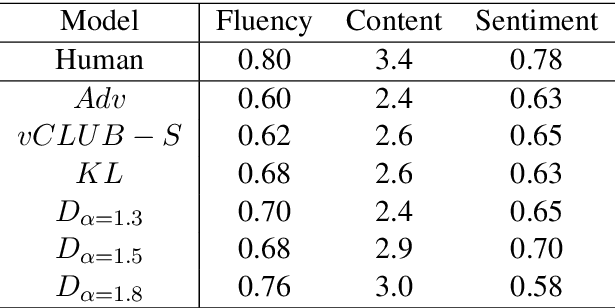

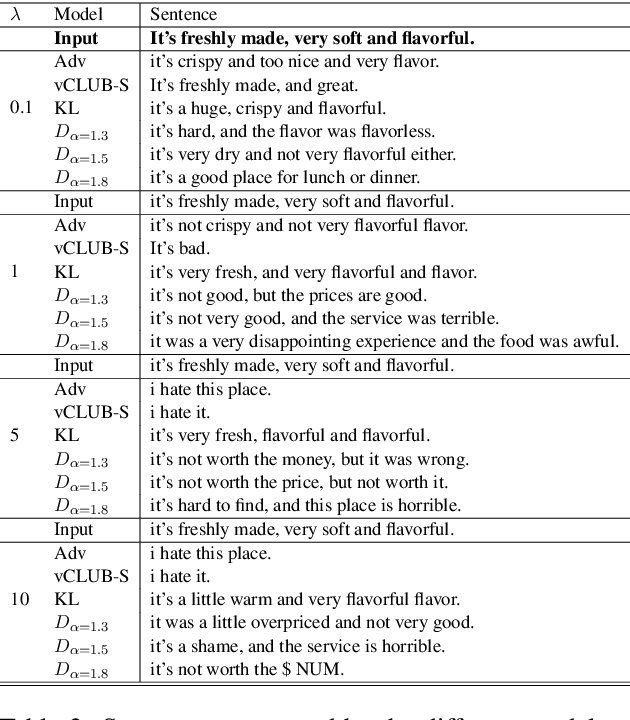
Learning disentangled representations of textual data is essential for many natural language tasks such as fair classification, style transfer and sentence generation, among others. The existent dominant approaches in the context of text data {either rely} on training an adversary (discriminator) that aims at making attribute values difficult to be inferred from the latent code {or rely on minimising variational bounds of the mutual information between latent code and the value attribute}. {However, the available methods suffer of the impossibility to provide a fine-grained control of the degree (or force) of disentanglement.} {In contrast to} {adversarial methods}, which are remarkably simple, although the adversary seems to be performing perfectly well during the training phase, after it is completed a fair amount of information about the undesired attribute still remains. This paper introduces a novel variational upper bound to the mutual information between an attribute and the latent code of an encoder. Our bound aims at controlling the approximation error via the Renyi's divergence, leading to both better disentangled representations and in particular, a precise control of the desirable degree of disentanglement {than state-of-the-art methods proposed for textual data}. Furthermore, it does not suffer from the degeneracy of other losses in multi-class scenarios. We show the superiority of this method on fair classification and on textual style transfer tasks. Additionally, we provide new insights illustrating various trade-offs in style transfer when attempting to learn disentangled representations and quality of the generated sentence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge