A New Spectral Clustering Algorithm
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2017


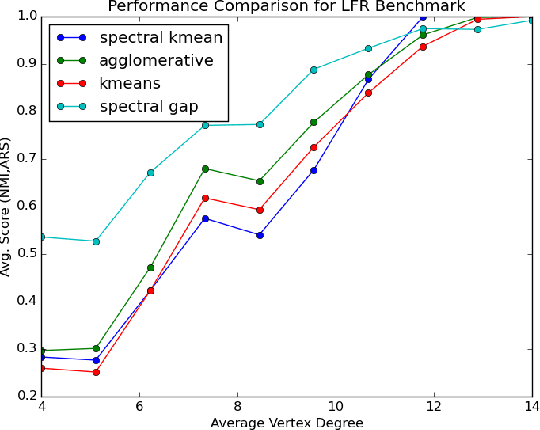
We present a new clustering algorithm that is based on searching for natural gaps in the components of the lowest energy eigenvectors of the Laplacian of a graph. In comparing the performance of the proposed method with a set of other popular methods (KMEANS, spectral-KMEANS, and an agglomerative method) in the context of the Lancichinetti-Fortunato-Radicchi (LFR) Benchmark for undirected weighted overlapping networks, we find that the new method outperforms the other spectral methods considered in certain parameter regimes. Finally, in an application to climate data involving one of the most important modes of interannual climate variability, the El Nino Southern Oscillation phenomenon, we demonstrate the ability of the new algorithm to readily identify different flavors of the phenomenon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge