A New Fundamental Evidence of Non-Classical Structure in the Combination of Natural Concepts
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2015
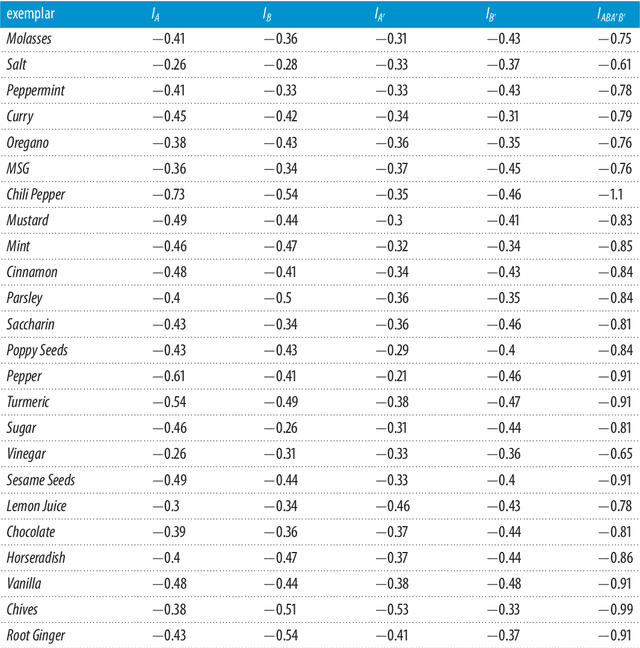

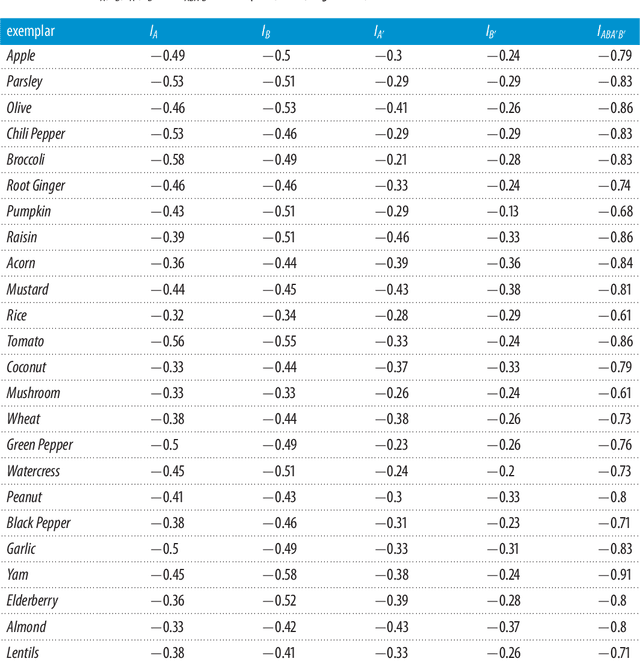
We recently performed cognitive experiments on conjunctions and negations of two concepts with the aim of investigating the combination problem of concepts. Our experiments confirmed the deviations (conceptual vagueness, underextension, overextension, etc.) from the rules of classical (fuzzy) logic and probability theory observed by several scholars in concept theory, while our data were successfully modeled in a quantum-theoretic framework developed by ourselves. In this paper, we isolate a new, very stable and systematic pattern of violation of classicality that occurs in concept combinations. In addition, the strength and regularity of this non-classical effect leads us to believe that it occurs at a more fundamental level than the deviations observed up to now. It is our opinion that we have identified a deep non-classical mechanism determining not only how concepts are combined but, rather, how they are formed. We show that this effect can be faithfully modeled in a two-sector Fock space structure, and that it can be exactly explained by assuming that human thought is the supersposition of two processes, a 'logical reasoning', guided by 'logic', and a 'conceptual reasoning' guided by 'emergence', and that the latter generally prevails over the former. All these findings provide a new fundamental support to our quantum-theoretic approach to human cognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge