A new BART prior for flexible modeling with categorical predictors
Paper and Code
Nov 08, 2022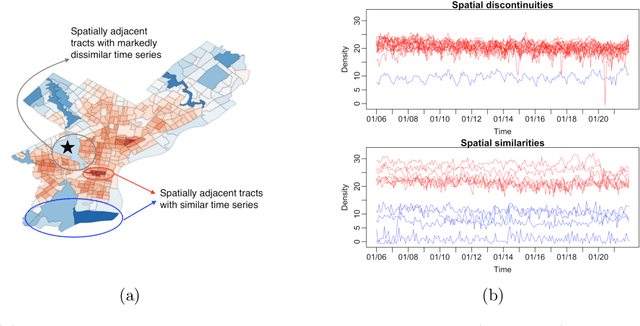

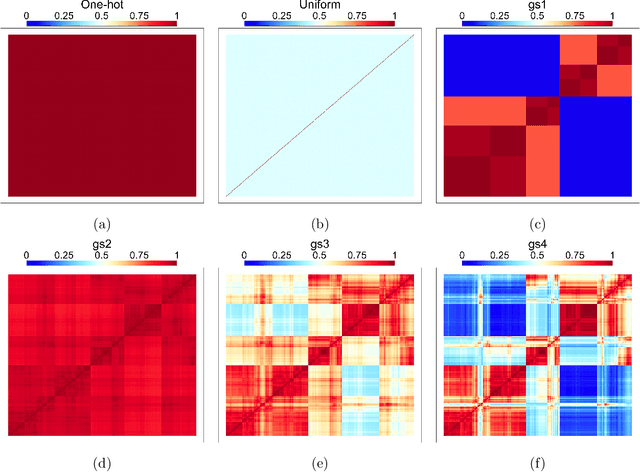
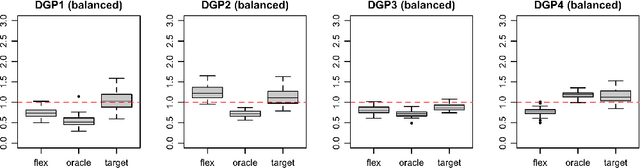
Default implementations of Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART) represent categorical predictors using several binary indicators, one for each level of each categorical predictor. Regression trees built with these indicators partition the levels using a ``remove one a time strategy.'' Unfortunately, the vast majority of partitions of the levels cannot be built with this strategy, severely limiting BART's ability to ``borrow strength'' across groups of levels. We overcome this limitation with a new class of regression tree and a new decision rule prior that can assign multiple levels to both the left and right child of a decision node. Motivated by spatial applications with areal data, we introduce a further decision rule prior that partitions the areas into spatially contiguous regions by deleting edges from random spanning trees of a suitably defined network. We implemented our new regression tree priors in the flexBART package, which, compared to existing implementations, often yields improved out-of-sample predictive performance without much additional computational burden. We demonstrate the efficacy of flexBART using examples from baseball and the spatiotemporal modeling of crime.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge