A Macrocolumn Architecture Implemented with Temporal (Spiking) Neurons
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2022
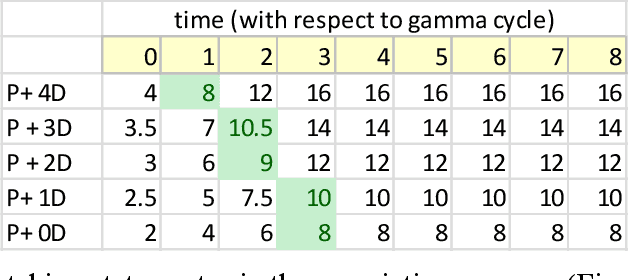
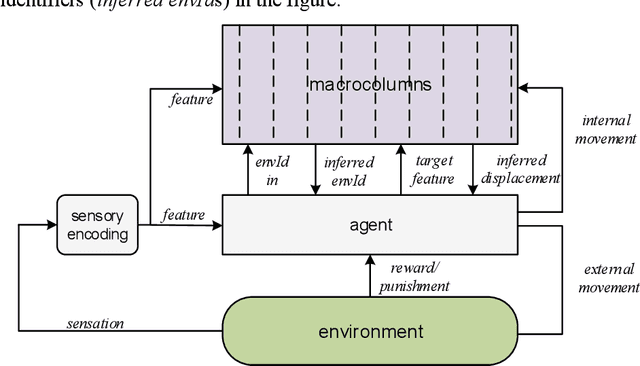
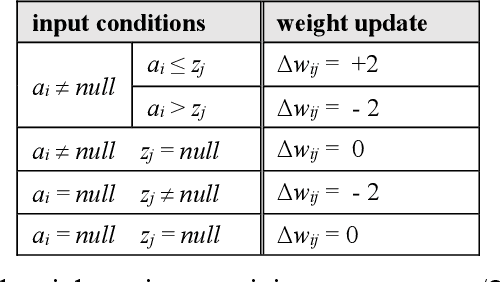
With the long-term goal of reverse-architecting the computational brain from the bottom up, the focus of this document is the macrocolumn abstraction layer. A basic macrocolumn architecture is developed by first describing its operation with a state machine model. Then state machine functions are implemented with spiking neurons that support temporal computation. The neuron model is based on active spiking dendrites and mirrors the Hawkins/Numenta neuron model. The architecture is demonstrated with a research benchmark in which an agent uses a macrocolumn to first learn and then navigate 2-d environments containing randomly placed features. Environments are represented in the macrocolumn as labeled directed graphs where edges connect features and labels indicate the relative displacements between them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge