A Hierarchical Approach to Multi-Energy Demand Response: From Electricity to Multi-Energy Applications
Paper and Code
May 05, 2020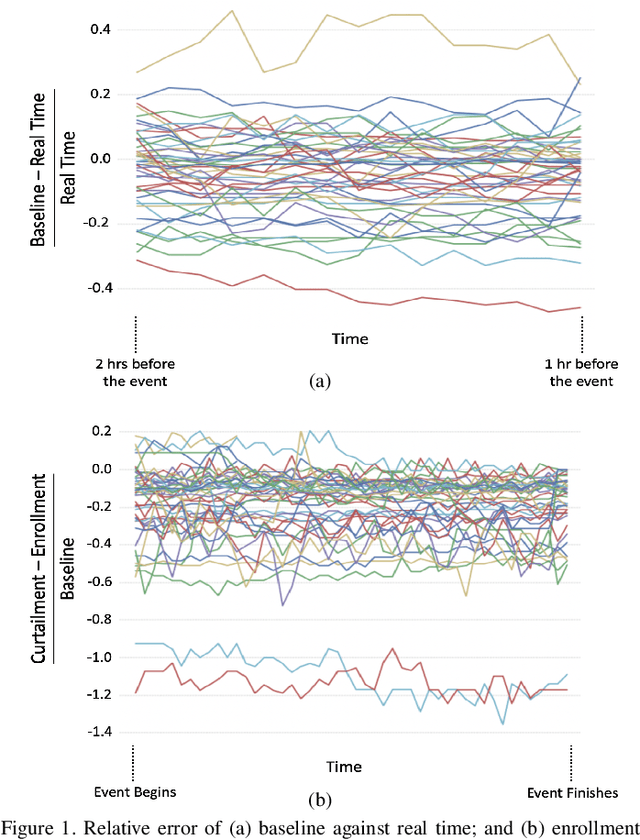
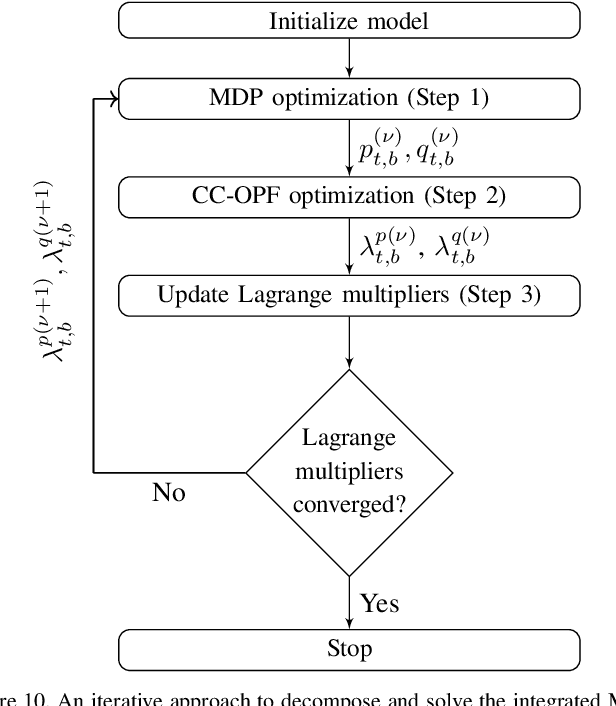
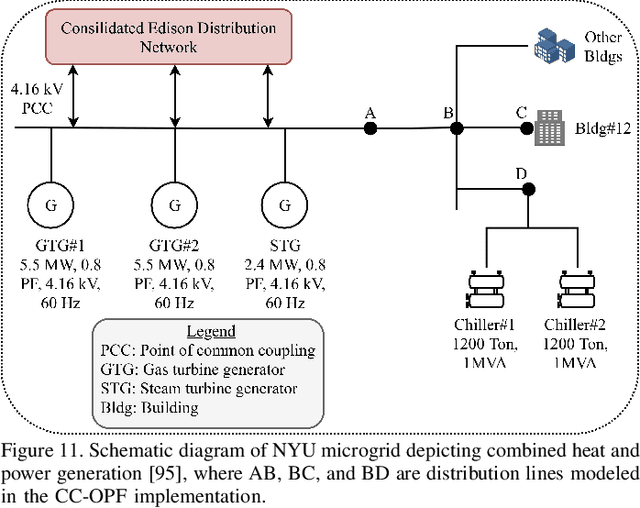
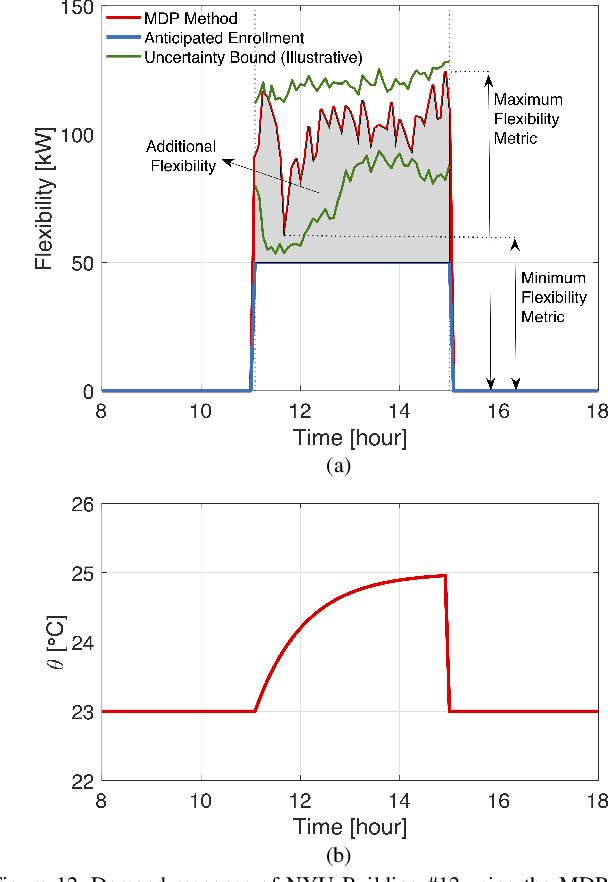
Due to proliferation of energy efficiency measures and availability of the renewable energy resources, traditional energy infrastructure systems (electricity, heat, gas) can no longer be operated in a centralized manner under the assumption that consumer behavior is inflexible, i.e. cannot be adjusted in return for an adequate incentive. To allow for a less centralized operating paradigm, consumer-end perspective and abilities should be integrated in current dispatch practices and accounted for in switching between different energy sources not only at the system but also at the individual consumer level. Since consumers are confined within different built environments, this paper looks into an opportunity to control energy consumption of an aggregation of many residential, commercial and industrial consumers, into an ensemble. This ensemble control becomes a modern demand response contributor to the set of modeling tools for multi-energy infrastructure systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge