A Hierarchical Approach to Active Pose Estimation
Paper and Code
Mar 08, 2022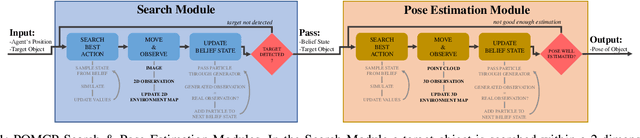
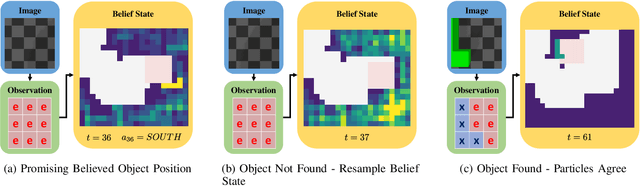
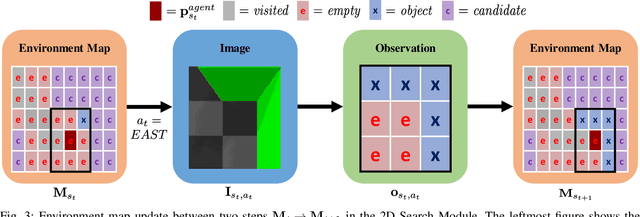

Creating mobile robots which are able to find and manipulate objects in large environments is an active topic of research. These robots not only need to be capable of searching for specific objects but also to estimate their poses often relying on environment observations, which is even more difficult in the presence of occlusions. Therefore, to tackle this problem we propose a simple hierarchical approach to estimate the pose of a desired object. An Active Visual Search module operating with RGB images first obtains a rough estimation of the object 2D pose, followed by a more computationally expensive Active Pose Estimation module using point cloud data. We empirically show that processing image features to obtain a richer observation speeds up the search and pose estimation computations, in comparison to a binary decision that indicates whether the object is or not in the current image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge