A giant with feet of clay: on the validity of the data that feed machine learning in medicine
Paper and Code
May 14, 2018
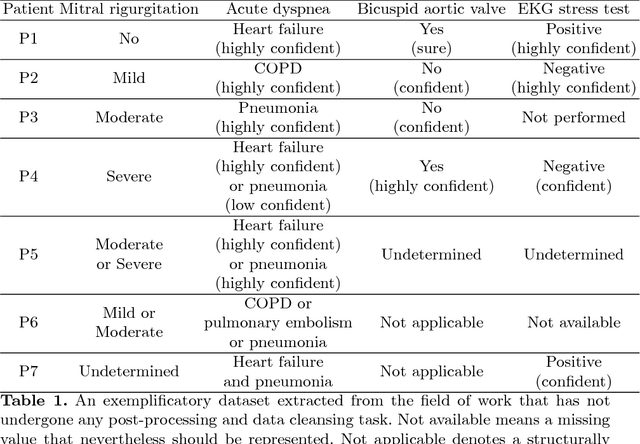


This paper considers the use of Machine Learning (ML) in medicine by focusing on the main problem that this computational approach has been aimed at solving or at least minimizing: uncertainty. To this aim, we point out how uncertainty is so ingrained in medicine that it biases also the representation of clinical phenomena, that is the very input of ML models, thus undermining the clinical significance of their output. Recognizing this can motivate both medical doctors, in taking more responsibility in the development and use of these decision aids, and the researchers, in pursuing different ways to assess the value of these systems. In so doing, both designers and users could take this intrinsic characteristic of medicine more seriously and consider alternative approaches that do not "sweep uncertainty under the rug" within an objectivist fiction, which everyone can come up by believing as true.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge