A Feasibility Study on Opportunistic Rainfall Measurement From Satellite TV Broadcasts
Paper and Code
Mar 08, 2023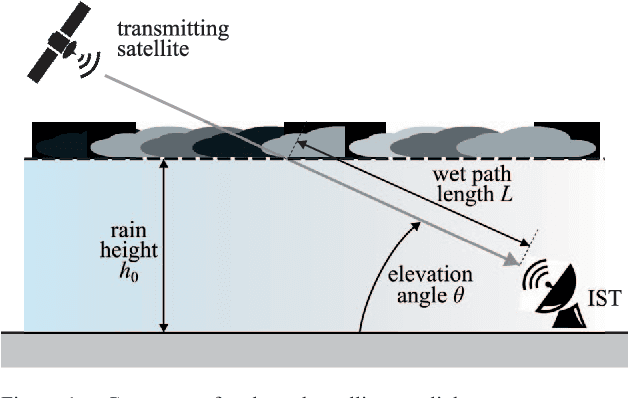
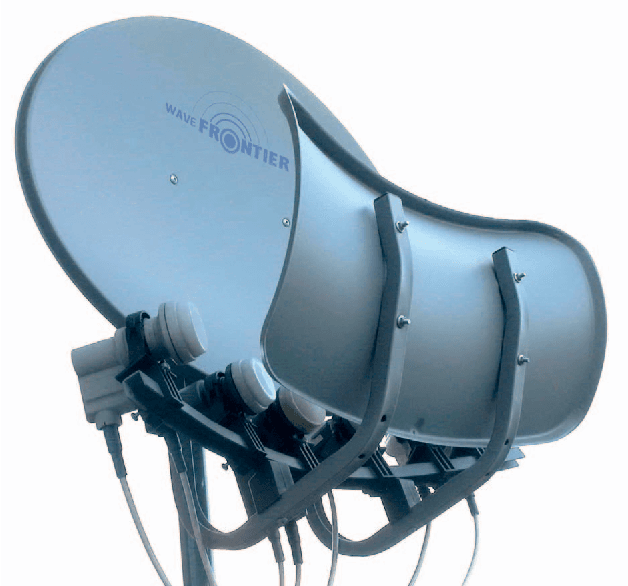

Rainfall precipitation maps are usually derived based on the measurements collected by classical weather devices, such as rain gauges and weather stations. This article aims to show the benefits obtained by opportunistic rainfall measurements based on signal strength measurements provided by commercial-grade satellite terminals (e.g., used in TV broadcasting). To assess not only the feasibility of this approach, with significant advantages in terms of capital and operational expenditure, but also improvements in terms of accuracy, we focus on a case study for agricultural applications using a Gaussian-modeled synthetic rain over a specific, real-world test area.
* published on URSI Radio Science Letters, vol. 4, 2022 * 5 pages, 7 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge