A distributed block coordinate descent method for training $l_1$ regularized linear classifiers
Paper and Code
Mar 16, 2015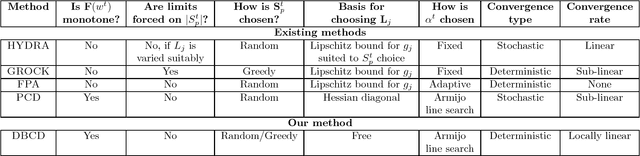
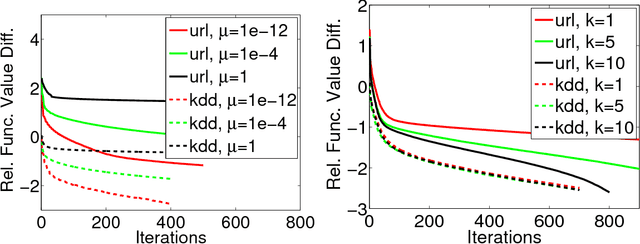
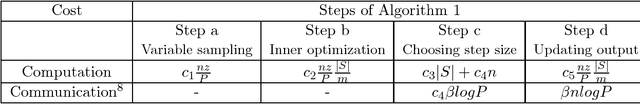
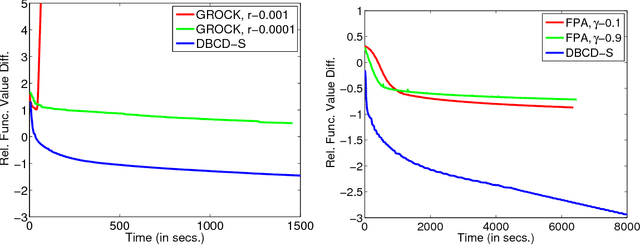
Distributed training of $l_1$ regularized classifiers has received great attention recently. Most existing methods approach this problem by taking steps obtained from approximating the objective by a quadratic approximation that is decoupled at the individual variable level. These methods are designed for multicore and MPI platforms where communication costs are low. They are inefficient on systems such as Hadoop running on a cluster of commodity machines where communication costs are substantial. In this paper we design a distributed algorithm for $l_1$ regularization that is much better suited for such systems than existing algorithms. A careful cost analysis is used to support these points and motivate our method. The main idea of our algorithm is to do block optimization of many variables on the actual objective function within each computing node; this increases the computational cost per step that is matched with the communication cost, and decreases the number of outer iterations, thus yielding a faster overall method. Distributed Gauss-Seidel and Gauss-Southwell greedy schemes are used for choosing variables to update in each step. We establish global convergence theory for our algorithm, including Q-linear rate of convergence. Experiments on two benchmark problems show our method to be much faster than existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge