A Density Ratio Approach to Language Model Fusion in End-To-End Automatic Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2020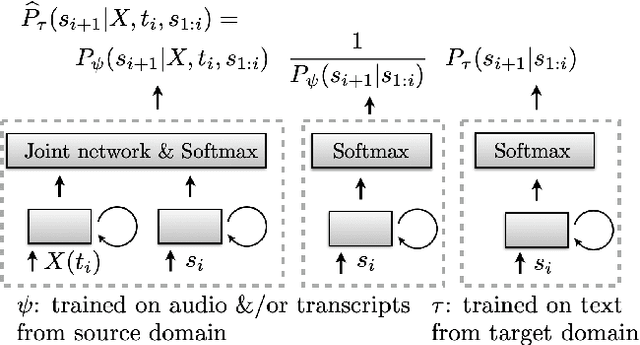
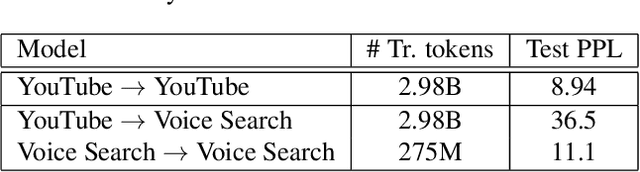
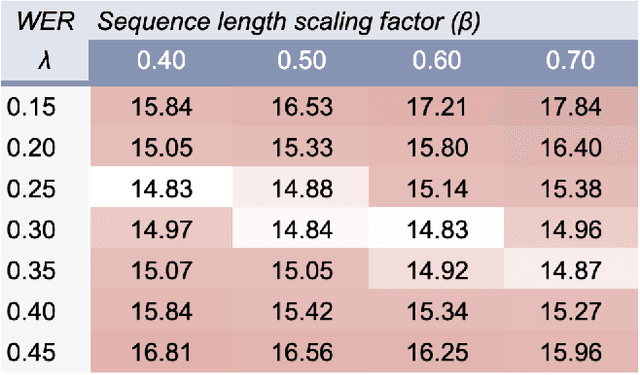
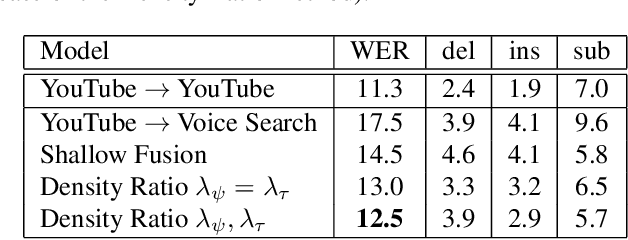
This article describes a density ratio approach to integrating external Language Models (LMs) into end-to-end models for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). Applied to a Recurrent Neural Network Transducer (RNN-T) ASR model trained on a given domain, a matched in-domain RNN-LM, and a target domain RNN-LM, the proposed method uses Bayes' Rule to define RNN-T posteriors for the target domain, in a manner directly analogous to the classic hybrid model for ASR based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) or LSTMs in the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) framework (Bourlard & Morgan, 1994). The proposed approach is evaluated in cross-domain and limited-data scenarios, for which a significant amount of target domain text data is used for LM training, but only limited (or no) {audio, transcript} training data pairs are used to train the RNN-T. Specifically, an RNN-T model trained on paired audio & transcript data from YouTube is evaluated for its ability to generalize to Voice Search data. The Density Ratio method was found to consistently outperform the dominant approach to LM and end-to-end ASR integration, Shallow Fusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge