A Crossover That Matches Diverse Parents Together in Evolutionary Algorithms
Paper and Code
May 08, 2021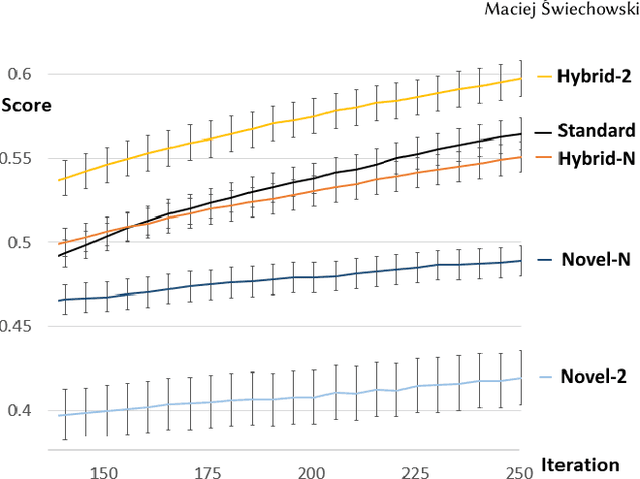
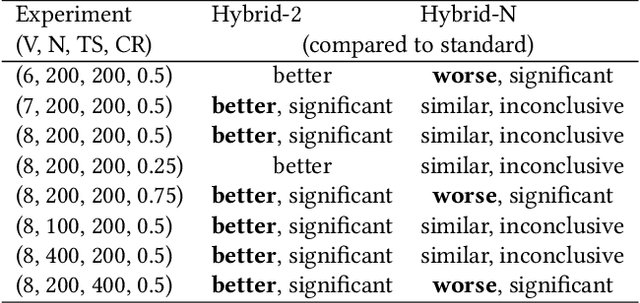
Crossover and mutation are the two main operators that lead to new solutions in evolutionary approaches. In this article, a new method of performing the crossover phase is presented. The problem of choice is evolutionary decision tree construction. The method aims at finding such individuals that together complement each other. Hence we say that they are diversely specialized. We propose the way of calculating the so-called complementary fitness. In several empirical experiments, we evaluate the efficacy of the method proposed in four variants and compare it to a fitness-rank-based approach. One variant emerges clearly as the best approach, whereas the remaining ones are below the baseline.
* Accepted to GECCO 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge