A Comparison of Reward Functions in Q-Learning Applied to a Cart Position Problem
Paper and Code
May 25, 2021

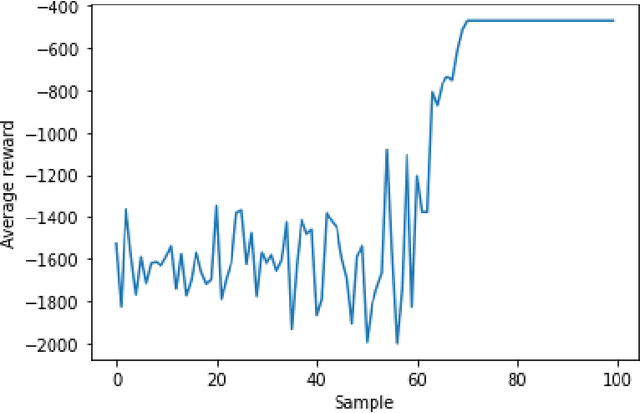

Growing advancements in reinforcement learning has led to advancements in control theory. Reinforcement learning has effectively solved the inverted pendulum problem and more recently the double inverted pendulum problem. In reinforcement learning, our agents learn by interacting with the control system with the goal of maximizing rewards. In this paper, we explore three such reward functions in the cart position problem. This paper concludes that a discontinuous reward function that gives non-zero rewards to agents only if they are within a given distance from the desired position gives the best results.
* 19 pages, 15 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge