A Comparative Study of Some Central Notions of ASPIC+ and DeLP
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2019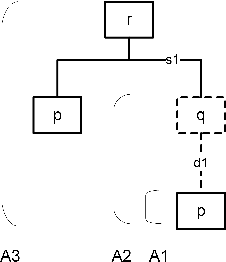
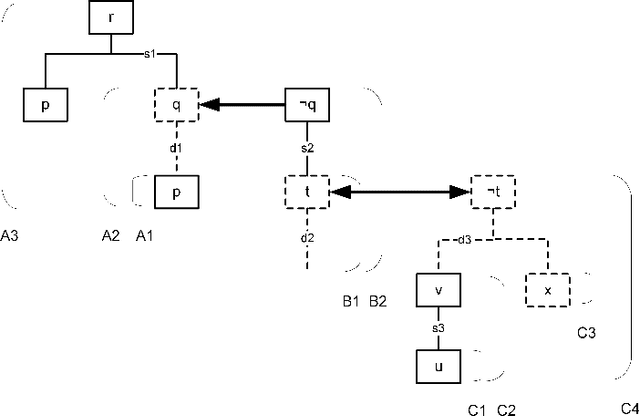
This paper formally compares some central notions from two well-known formalisms for rule-based argumentation, DeLP and ASPIC+. The comparisons especially focus on intuitive adequacy and inter-translatability, consistency, and closure properties. As for differences in the definitions of arguments and attack, it turns out that DeLP's definitions are intuitively appealing but that they may not fully comply with Caminada and Amgoud's rationality postulates of strict closure and indirect consistency. For some special cases, the DeLP definitions are shown to fare better than ASPIC+. Next, it is argued that there are reasons to consider a variant of DeLP with grounded semantics, since in some examples its current notion of warrant arguably has counterintuitive consequences and may lead to sets of warranted arguments that are not admissible. Finally, under some minimality and consistency assumptions on ASPIC+ arguments, a one-to-many correspondence between ASPIC+ arguments and DeLP arguments is identified in such a way that if the DeLP warranting procedure is changed to grounded semantics, then DeLP notion of warrant and ASPIC+'s notion of justification are equivalent. This result is proven for three alternative definitions of attack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge