Zhongbao Zhou
Satellite image data downlink scheduling problem with family attribute: Model &Algorithm
Jul 04, 2022



Abstract:The asynchronous development between the observation capability and the transition capability results in that an original image data (OID) formed by one-time observation cannot be completely transmitted in one transmit chance between the EOS and GS (named as a visible time window, VTW). It needs to segment the OID to several segmented image data (SID) and then transmits them in several VTWs, which enriches the extension of satellite image data downlink scheduling problem (SIDSP). We define the novel SIDSP as satellite image data downlink scheduling problem with family attribute (SIDSPWFA), in which some big OID is segmented by a fast segmentation operator first, and all SID and other no-segmented OID is transmitted in the second step. Two optimization objectives, the image data transmission failure rate (FR) and the segmentation times (ST), are then designed to formalize SIDSPWFA as a bi-objective discrete optimization model. Furthermore, a bi-stage differential evolutionary algorithm(DE+NSGA-II) is developed holding several bi-stage operators. Extensive simulation instances show the efficiency of models, strategies, algorithms and operators is analyzed in detail.
Multi-strip observation scheduling problem for ac-tive-imaging agile earth observation satellites
Jul 04, 2022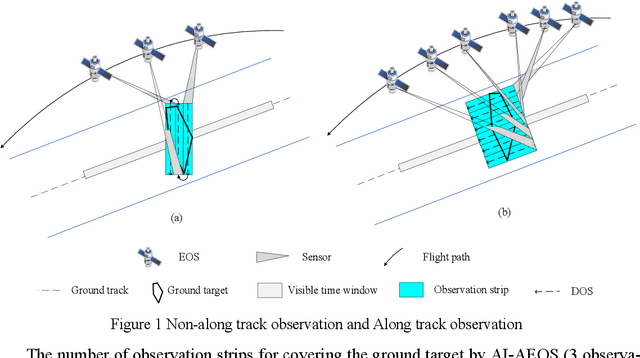
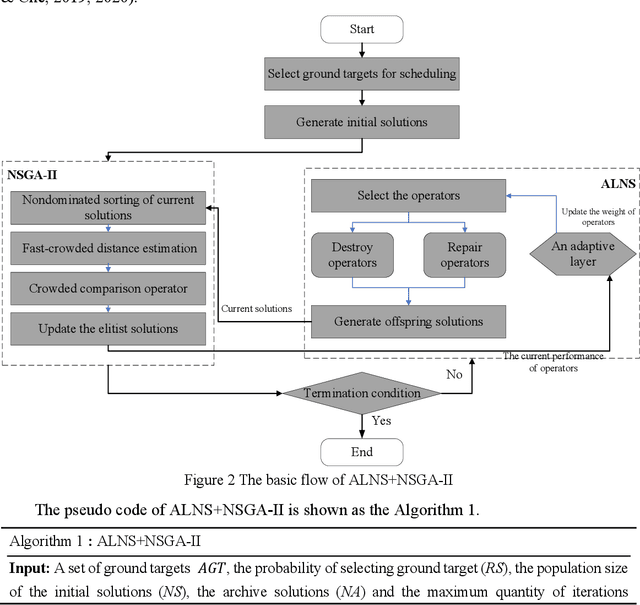
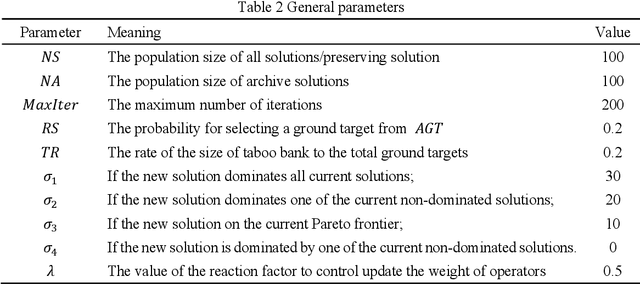
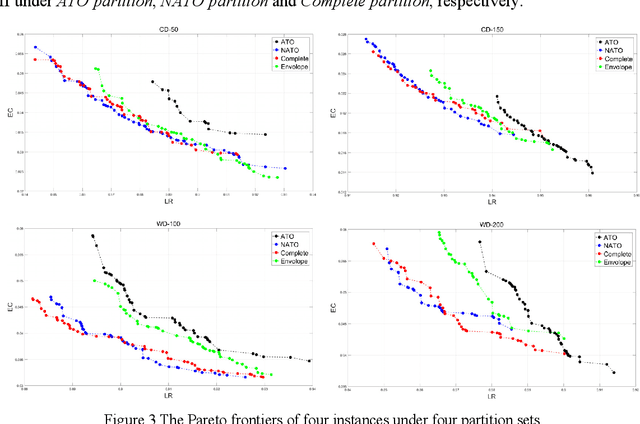
Abstract:Active-imaging agile earth observation satellite (AI-AEOS) is a new generation agile earth observation satellite (AEOS). With renewed capabilities in observation and active im-aging, AI-AEOS improves upon the observation capabilities of AEOS and provide additional ways to observe ground targets. This however makes the observation scheduling problem for these agile earth observation satellite more complex, especially when considering multi-strip ground targets. In this paper, we investigate the multi-strip observation scheduling problem for an active-image agile earth observation satellite (MOSP). A bi-objective optimization model is presented for MOSP along with an adaptive bi-objective memetic algorithm which integrates the combined power of an adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm (ALNS) and a nondominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II). Results of extensive computa-tional experiments are presented which disclose that ALNS and NSGA-II when worked in unison produced superior outcomes. Our model is more versatile than existing models and provide enhanced capabilities in applied problem solving.
Three multi-objective memtic algorithms for observation scheduling problem of active-imaging AEOS
Jul 04, 2022



Abstract:Observation scheduling problem for agile earth observation satellites (OSPFAS) plays a critical role in management of agile earth observation satellites (AEOSs). Active imaging enriches the extension of OSPFAS, we call the novel problem as observation scheduling problem for AEOS with variable image duration (OSWVID). A cumulative image quality and a detailed energy consumption is proposed to build OSWVID as a bi-objective optimization model. Three multi-objective memetic algorithms, PD+NSGA-II, LA+NSGA-II and ALNS+NSGA-II, are then designed to solve OSWVID. Considering the heuristic knowledge summarized in our previous research, several operators are designed for improving these three algorithms respectively. Based on existing instances, we analyze the critical parameters optimization, operators evolution, and efficiency of these three algorithms according to extensive simulation experiments.
Satellite downlink scheduling under breakpoint resume mode
Jul 04, 2022



Abstract:A novel problem called satellite downlink scheduling problem (SDSP) under breakpoint resume mode (SDSP-BRM) is studied in our paper. Compared to the traditional SDSP where an imaging data has to be completely downloaded at one time, SDSP-BRM allows the data of an imaging data be broken into a number of pieces which can be downloaded in different playback windows. By analyzing the characteristics of SDSP-BRM, we first propose a mixed integer programming model for its formulation and then prove the NP-hardness of SDSP-BRM. To solve the problem, we design a simple and effective heuristic algorithm (SEHA) where a number of problem-tailored move operators are proposed for local searching. Numerical results on a set of well-designed scenarios demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed algorithm in comparison to the general purpose CPLEX solver. We conduct additional experiments to shed light on the impact of the segmental strategy on the overall performance of the proposed SEHA.
An adaptive bi-objective optimization algorithm for the satellite image data downlink scheduling problem considering request split
Jun 28, 2022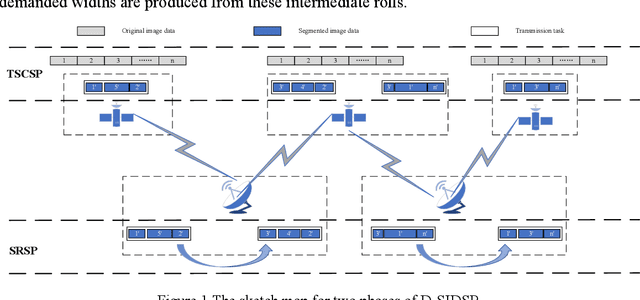
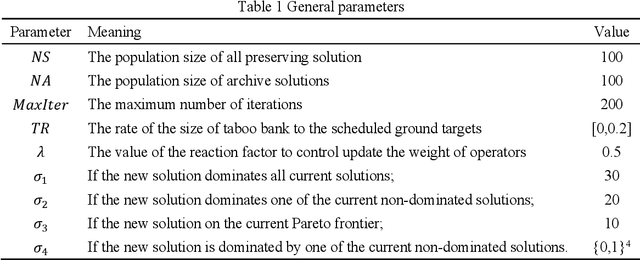
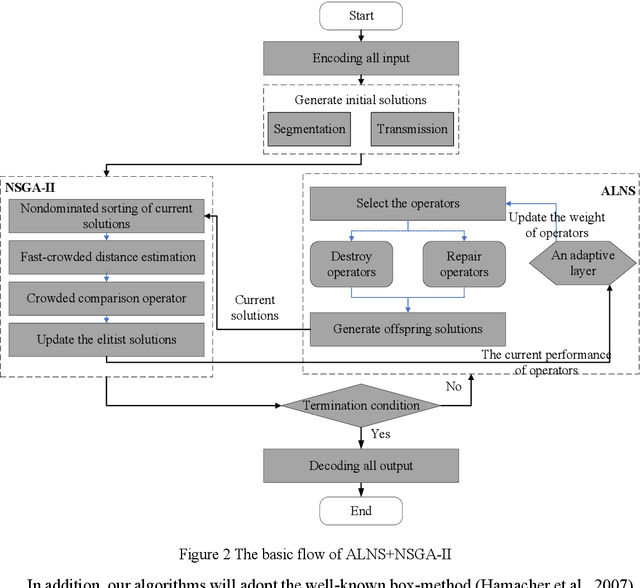
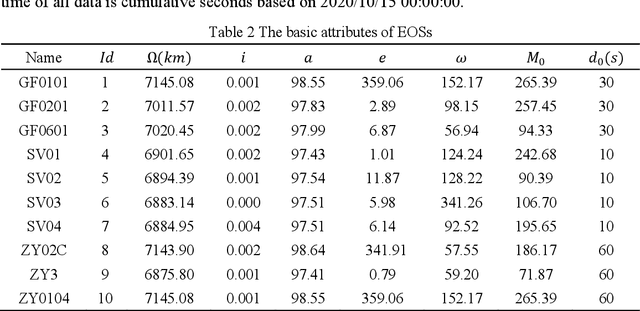
Abstract:The satellite image data downlink scheduling problem (SIDSP) is well studied in literature for traditional satellites. With recent developments in satellite technology, SIDSP for modern satellites became more complicated, adding new dimensions of complexities and additional opportunities for the effective use of the satellite. In this paper, we introduce the dynamic two-phase satellite image data downlink scheduling problem (D-SIDSP) which combines two interlinked operations of image data segmentation and image data downlink, in a dynamic way, and thereby offering additional modelling flexibility and renewed capabilities. D-SIDSP is formulated as a bi-objective problem of optimizing the image data transmission rate and the service-balance degree. Harnessing the power of an adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm (ALNS) with a nondominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II), an adaptive bi-objective memetic algorithm, ALNS+NSGA-II, is developed to solve D-SIDSP. Results of extensive computational experiments carried out using benchmark instances are also presented. Our experimental results disclose that the algorithm ALNS+NSGA-II is a viable alternative to solve D-SIDSP more efficiently and demonstrates superior outcomes based on various performance metrics. The paper also offers new benchmark instances for D-SIDSP that can be used in future research works on the topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge