Zabir Al Nazi
†DAGGER: Distractor-Aware Graph Generation for Executable Reasoning in Math Problems
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting is widely adopted for mathematical problem solving, including in low-resource languages, yet its behavior under irrelevant context remains underexplored. To systematically study this challenge, we introduce DISTRACTMATH-BN, a Bangla benchmark that augments MGSM and MSVAMP with semantically coherent but computationally irrelevant information. Evaluating seven models ranging from 3B to 12B parameters, we observe substantial performance degradation under distractors: standard models drop by up to 41 points, while reasoning-specialized models decline by 14 to 20 points despite consuming five times more tokens. We propose †DAGGER, which reformulates mathematical problem solving as executable computational graph generation with explicit modeling of distractor nodes. Fine-tuning Gemma-3 models using supervised fine-tuning followed by Group Relative Policy Optimization achieves comparable weighted accuracy on augmented benchmarks while using 89 percent fewer tokens than reasoning models. Importantly, this robustness emerges without explicit training on distractor-augmented examples. Our results suggest that enforcing structured intermediate representations improves robustness and inference efficiency in mathematical reasoning compared to free-form approaches, particularly in noisy, low-resource settings.
PII-VisBench: Evaluating Personally Identifiable Information Safety in Vision Language Models Along a Continuum of Visibility
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) are increasingly integrated into privacy-critical domains, yet existing evaluations of personally identifiable information (PII) leakage largely treat privacy as a static extraction task and ignore how a subject's online presence--the volume of their data available online--influences privacy alignment. We introduce PII-VisBench, a novel benchmark containing 4000 unique probes designed to evaluate VLM safety through the continuum of online presence. The benchmark stratifies 200 subjects into four visibility categories: high, medium, low, and zero--based on the extent and nature of their information available online. We evaluate 18 open-source VLMs (0.3B-32B) based on two key metrics: percentage of PII probing queries refused (Refusal Rate) and the fraction of non-refusal responses flagged for containing PII (Conditional PII Disclosure Rate). Across models, we observe a consistent pattern: refusals increase and PII disclosures decrease (9.10% high to 5.34% low) as subject visibility drops. We identify that models are more likely to disclose PII for high-visibility subjects, alongside substantial model-family heterogeneity and PII-type disparities. Finally, paraphrasing and jailbreak-style prompts expose attack and model-dependent failures, motivating visibility-aware safety evaluation and training interventions.
Are Vision Language Models Cross-Cultural Theory of Mind Reasoners?
Dec 19, 2025
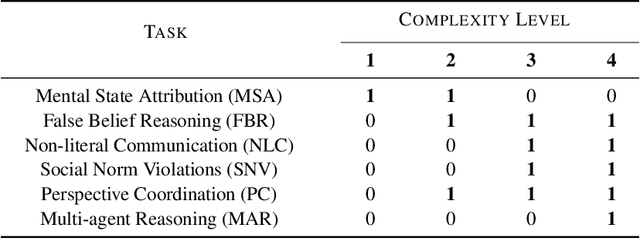
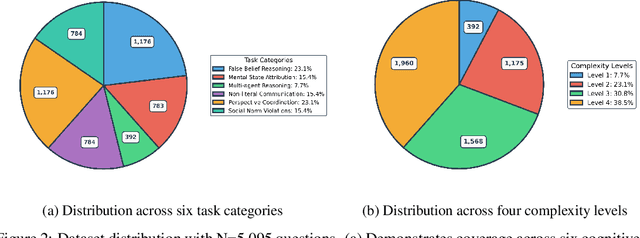
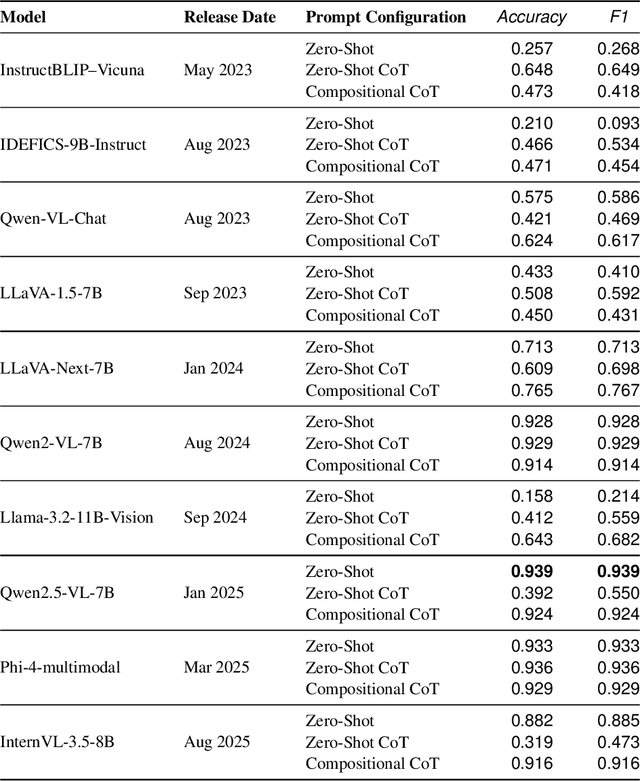
Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) -- the ability to attribute beliefs, desires, and emotions to others -- is fundamental for human social intelligence, yet remains a major challenge for artificial agents. Existing Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are increasingly applied in socially grounded tasks, but their capacity for cross-cultural ToM reasoning is largely unexplored. In this work, we introduce CulturalToM-VQA, a new evaluation benchmark containing 5095 questions designed to probe ToM reasoning across diverse cultural contexts through visual question answering. The dataset captures culturally grounded cues such as rituals, attire, gestures, and interpersonal dynamics, enabling systematic evaluation of ToM reasoning beyond Western-centric benchmarks. Our dataset is built through a VLM-assisted human-in-the-loop pipeline, where human experts first curate culturally rich images across traditions, rituals, and social interactions; a VLM then assist in generating structured ToM-focused scene descriptions, which are refined into question-answer pairs spanning a taxonomy of six ToM tasks and four graded complexity levels. The resulting dataset covers diverse theory of mind facets such as mental state attribution, false belief reasoning, non-literal communication, social norm violations, perspective coordination, and multi-agent reasoning.
Byakto Speech: Real-time long speech synthesis with convolutional neural network: Transfer learning from English to Bangla
May 31, 2021
Abstract:Speech synthesis is one of the challenging tasks to automate by deep learning, also being a low-resource language there are very few attempts at Bangla speech synthesis. Most of the existing works can't work with anything other than simple Bangla characters script, very short sentences, etc. This work attempts to solve these problems by introducing Byakta, the first-ever open-source deep learning-based bilingual (Bangla and English) text to a speech synthesis system. A speech recognition model-based automated scoring metric was also proposed to evaluate the performance of a TTS model. We also introduce a test benchmark dataset for Bangla speech synthesis models for evaluating speech quality. The TTS is available at https://github.com/zabir-nabil/bangla-tts
Fibro-CoSANet: Pulmonary Fibrosis Prognosis Prediction using a Convolutional Self Attention Network
Apr 13, 2021
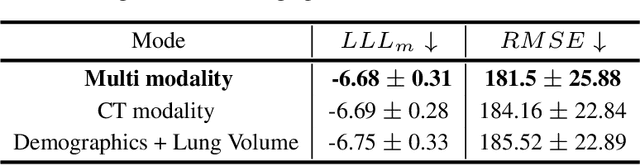

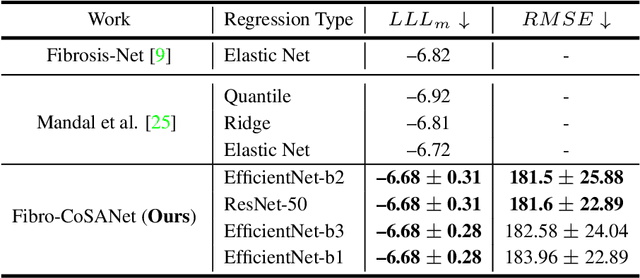
Abstract:Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a restrictive interstitial lung disease that causes lung function decline by lung tissue scarring. Although lung function decline is assessed by the forced vital capacity (FVC), determining the accurate progression of IPF remains a challenge. To address this challenge, we proposed Fibro-CoSANet, a novel end-to-end multi-modal learning-based approach, to predict the FVC decline. Fibro-CoSANet utilized CT images and demographic information in convolutional neural network frameworks with a stacked attention layer. Extensive experiments on the OSIC Pulmonary Fibrosis Progression Dataset demonstrated the superiority of our proposed Fibro-CoSANet by achieving the new state-of-the-art modified Laplace Log-Likelihood score of -6.68. This network may benefit research areas concerned with designing networks to improve the prognostic accuracy of IPF. The source-code for Fibro-CoSANet is available at: \url{https://github.com/zabir-nabil/Fibro-CoSANet}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge