Yurio Windiatmoko
Boarding House Renting Price Prediction Using Deep Neural Network Regression on Mobile Apps
Dec 31, 2020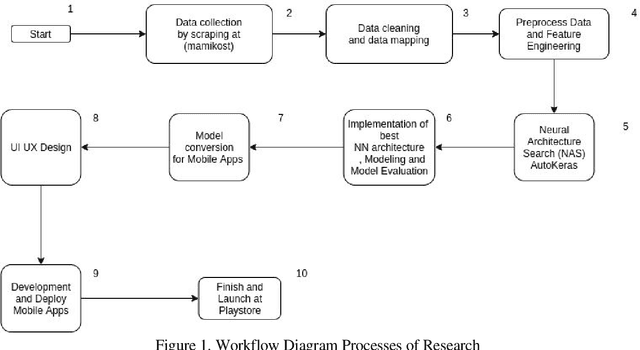
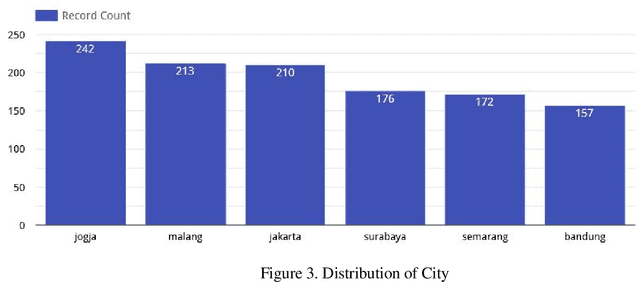
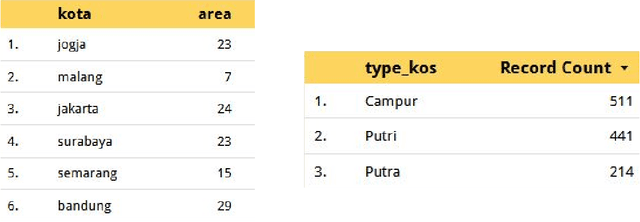
Abstract:Boarding house is the most important requirement, especially for college students who live far away from the city, place of his origin or house. However, the problem we see now is the uneven distribution of study places in Indonesia which 75% of the best top educational institutions come from the island of Java. So, students who are looking for boarding houses rent requires more effort in comparing the various aspects desired. They need to survey one by one to the boarding house they want, even though they can survey online, it still requires more effort to pay attention to the desired facilities one by one. Therefore, we then created an Mobile Application that can predict prices based on student needs by comparing several variables, namely city, area, type of boarding house, and facilities. So, students can easily estimate the ideal price. The results of this study prove that we have succeeded in predicting prices for boarding houses rent well based on the variables we have determined, and modeling that variables using Deep Neural Network Regression.
Optimizing Planning Service Territories by Dividing Into Compact Several Sub-areas Using Binary K-means Clustering According Vehicle Constraints
Oct 21, 2020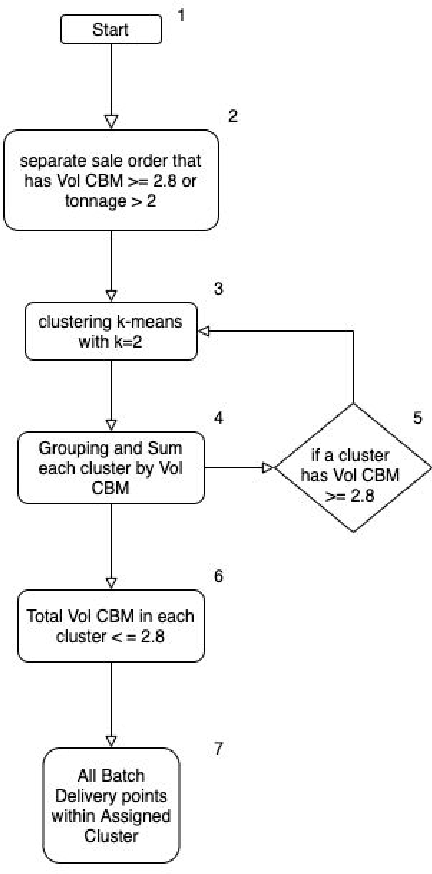
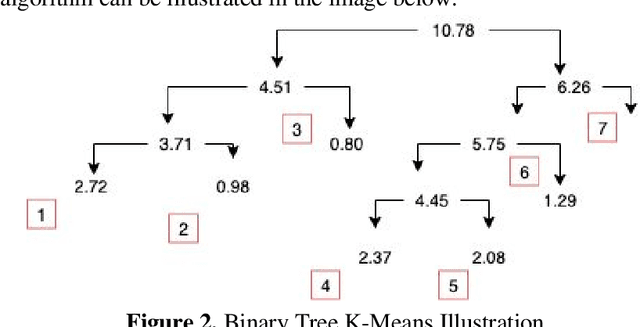
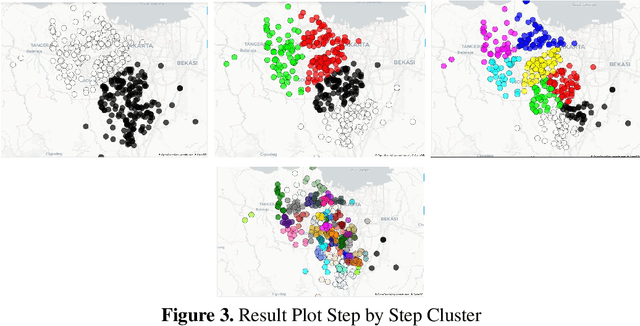
Abstract:VRP (Vehicle Routing Problem) is an NP hard problem, and it has attracted a lot of research interest. In contexts where vehicles have limited carrying capacity, such as volume and weight but needed to deliver items at various locations. Initially before creating a route, each vehicle needs a group of delivery points that are not exceeding their maximum capacity. Drivers tend to deliver only to certain areas. Cluster-based is one of the approaches to give a basis for generating tighter routes. In this paper we propose new algorithms for producing such clusters/groups that do not exceed vehicles maximum capacity. Our basic assumptions are each vehicle originates from a depot, delivers the items to the customers and returns to the depot, also the vehicles are homogeneous. This methods are able to compact sub-areas in each cluster. Computational results demonstrate the effectiveness of our new procedures, which are able to assist users to plan service territories and vehicle routes more efficiently.
Developing FB Chatbot Based on Deep Learning Using RASA Framework for University Enquiries
Sep 25, 2020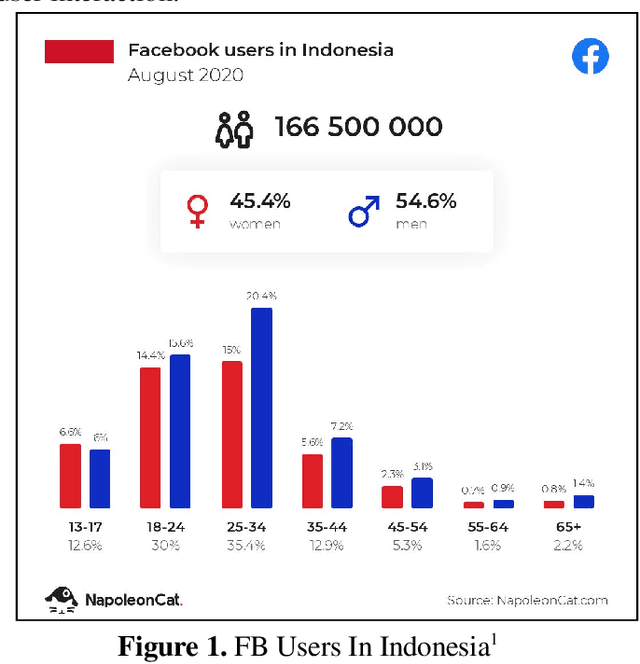

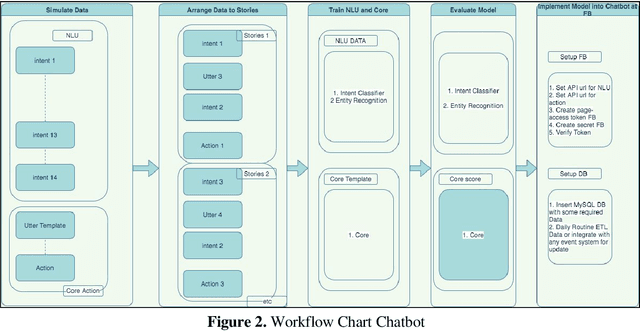

Abstract:Smart systems for Universities powered by Artificial Intelligence have been massively developed to help humans in various tasks. The chatbot concept is not something new in today society which is developing with recent technology. College students or candidates of college students often need actual information like asking for something to customer service, especially during this pandemic, when it is difficult to have an immediate face-to-face meeting. Chatbots are functionally helping in several things such as curriculum information, admission for new students, schedule info for any lecture courses, students grade information, and some adding features for Muslim worships schedule, also weather forecast information. This Chatbot is developed by Deep Learning models, which was adopted by an artificial intelligence model that replicates human intelligence with some specific training schemes. This kind of Deep Learning is based on RNN which has some specific memory savings scheme for the Deep Learning Model, specifically this chatbot using LSTM which already integrates by RASA framework. LSTM is also known as Long Short Term Memory which efficiently saves some required memory but will remove some memory that is not needed. This Chatbot uses the FB platform because of the FB users have already reached up to 60.8% of its entire population in Indonesia. Here's the chatbot only focuses on case studies at campus of the Magister Informatics FTI University of Islamic Indonesia. This research is a first stage development within fairly sufficient simulate data.
Image Captioning with Attention for Smart Local Tourism using EfficientNet
Sep 18, 2020
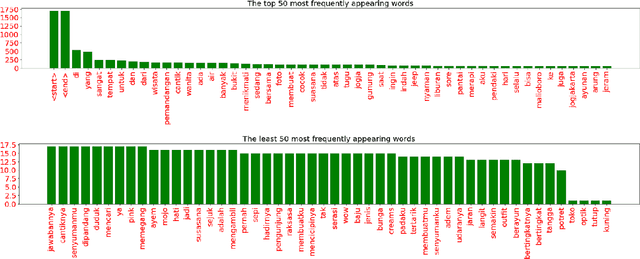
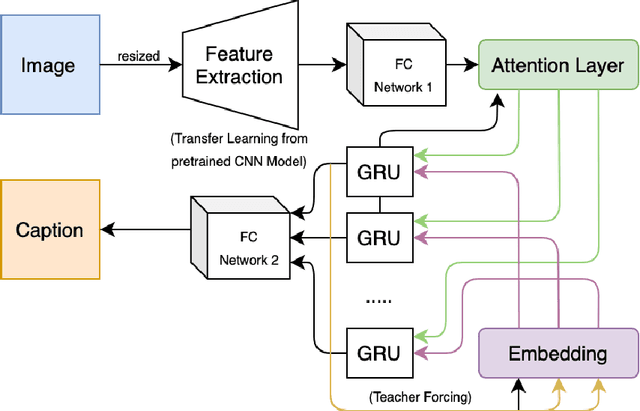
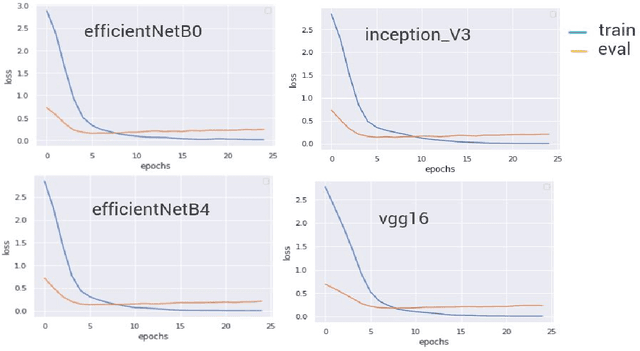
Abstract:Smart systems have been massively developed to help humans in various tasks. Deep Learning technologies push even further in creating accurate assistant systems due to the explosion of data lakes. One of the smart system tasks is to disseminate users needed information. This is crucial in the tourism sector to promote local tourism destinations. In this research, we design a model of local tourism specific image captioning, which later will support the development of AI-powered systems that assist various users. The model is developed using a visual Attention mechanism and uses the state-of-the-art feature extractor architecture EfficientNet. A local tourism dataset is collected and is used in the research, along with two different kinds of captions. Captions that describe the image literally and captions that represent human logical responses when seeing the image. This is done to make the captioning model more humane when implemented in the assistance system. We compared the performance of two different models using EfficientNet architectures (B0 and B4) with other well known VGG16 and InceptionV3. The best BLEU scores we get are 73.39 and 24.51 for the training set and the validation set respectively, using EfficientNetB0. The captioning result using the developed model shows that the model can produce logical caption for local tourism-related images
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge