Yong Khoo
A Random-Fern based Feature Approach for Image Matching
Jun 04, 2017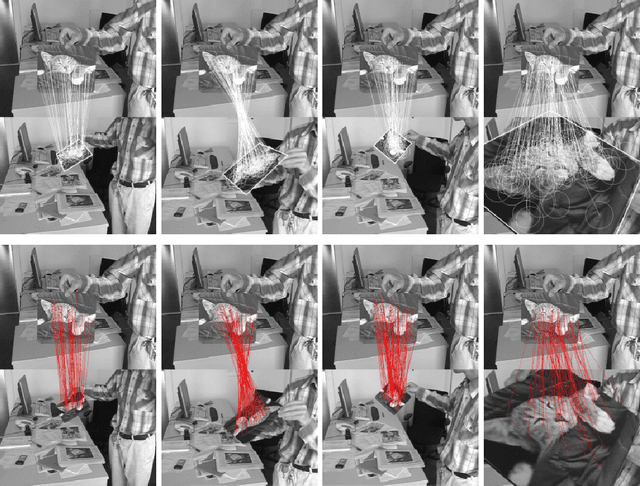
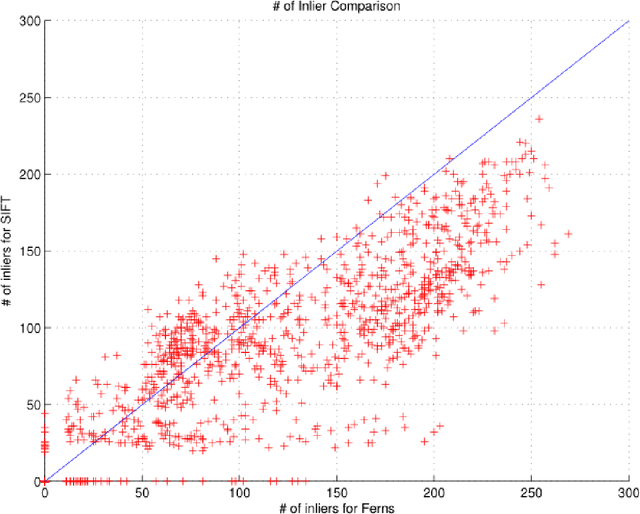

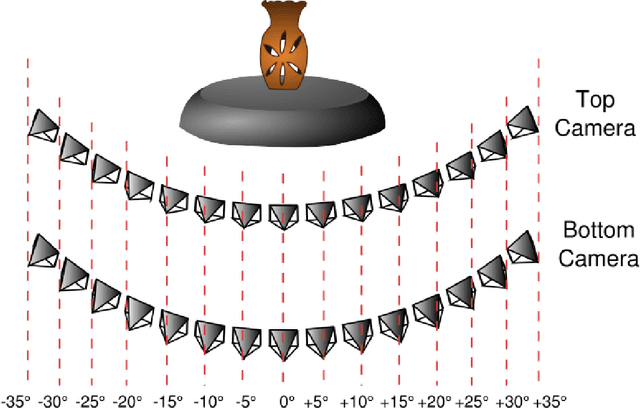
Abstract:Image or object recognition is an important task in computer vision. With the hight-speed processing power on modern platforms and the availability of mobile phones everywhere, millions of photos are uploaded to the internet per minute, it is critical to establish a generic framework for fast and accurate image processing for automatic recognition and information retrieval. In this paper, we proposed an efficient image recognition and matching method that is originally derived from Naive Bayesian classification method to construct a probabilistic model. Our method support real-time performance and have very high ability to distinguish similar images with high details. Experiments are conducted together with intensive comparison with state-of-the-arts on image matching, such as Ferns recognition and SIFT recognition. The results demonstrate satisfactory performance.
Automated Body Structure Extraction from Arbitrary 3D Mesh
May 16, 2017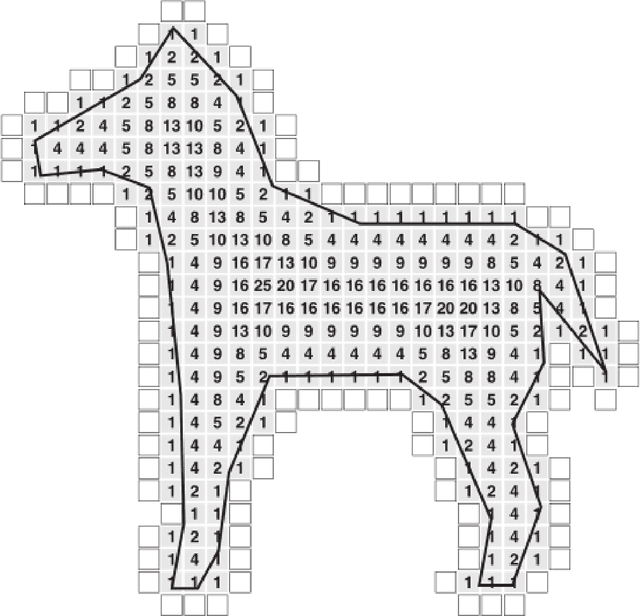
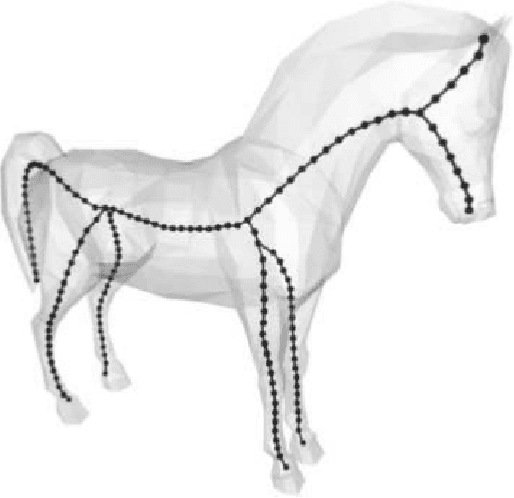
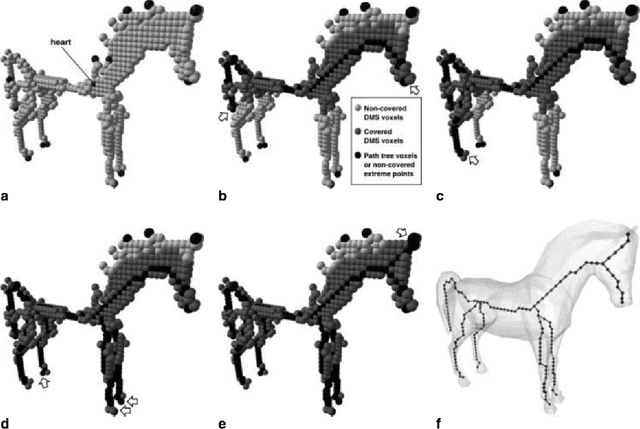

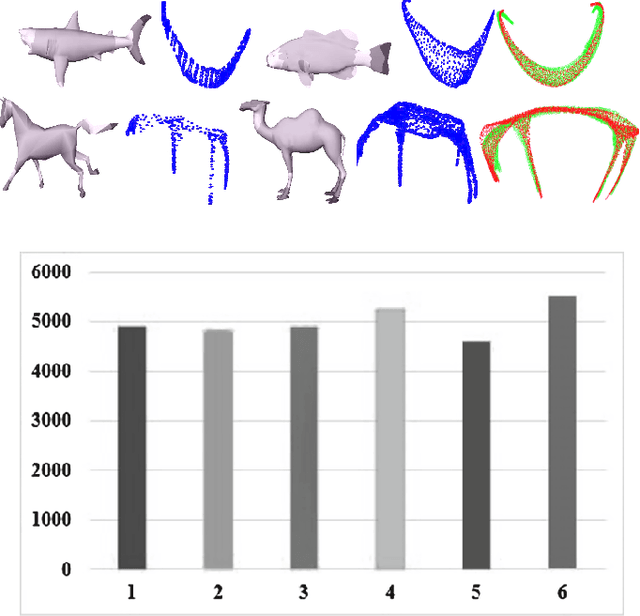
Abstract:This paper presents an automated method for 3D character skeleton extraction that can be applied for generic 3D shapes. Our work is motivated by the skeleton-based prior work on automatic rigging focused on skeleton extraction and can automatically aligns the extracted structure to fit the 3D shape of the given 3D mesh. The body mesh can be subsequently skinned based on the extracted skeleton and thus enables rigging process. In the experiment, we apply public dataset to drive the estimated skeleton from different body shapes, as well as the real data obtained from 3D scanning systems. Satisfactory results are obtained compared to the existing approaches.
A Correspondence Relaxation Approach for 3D Shape Reconstruction
May 14, 2017
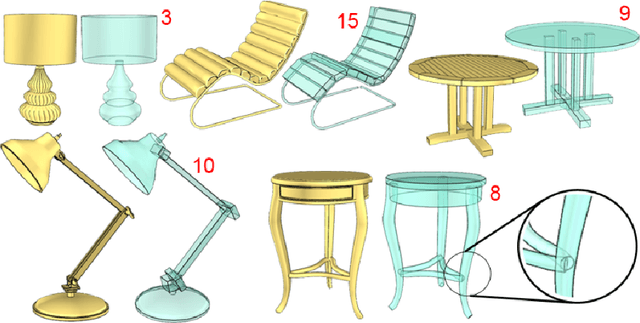
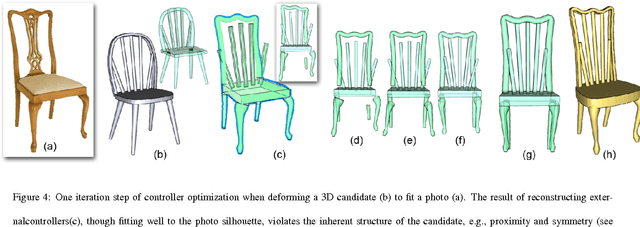
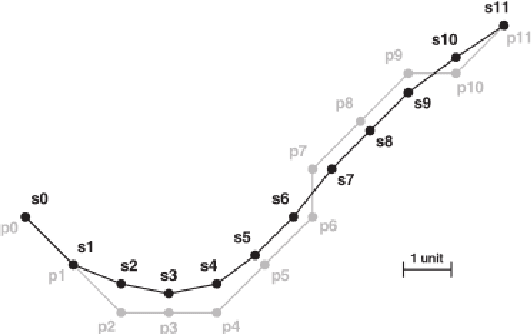
Abstract:This paper presents a new method for 3D shape reconstruction based on two existing methods. A 3D reconstruction from a single photograph is introduced by both papers: the first one uses a photograph and a set of existing 3D model to generate the 3D object in the photograph, while the second one uses a photograph and a selected similar model to create the 3D object in the photograph. According to their difference, we propose a relaxation based method for more accurate correspondence establishment and shape recovery. The experiment demonstrates promising results compared to the state-of-the-art work on 3D shape estimation.
Large Angle based Skeleton Extraction for 3D Animation
Aug 17, 2016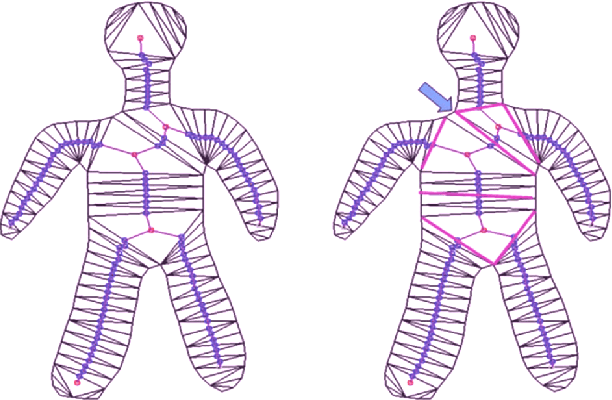
Abstract:In this paper, we present a solution for arbitrary 3D character deformation by investigating rotation angle of decomposition and preserving the mesh topology structure. In computer graphics, skeleton extraction and skeleton-driven animation is an active areas and gains increasing interests from researchers. The accuracy is critical for realistic animation and related applications. There have been extensive studies on skeleton based 3D deformation. However for the scenarios of large angle rotation of different body parts, it has been relatively less addressed by the state-of-the-art, which often yield unsatisfactory results. Besides 3D animation problems, we also notice for many 3D skeleton detection or tracking applications from a video or depth streams, large angle rotation is also a critical factor in the regression accuracy and robustness. We introduced a distortion metric function to quantify the surface curviness before and after deformation, which is a major clue for large angle rotation detection. The intensive experimental results show that our method is suitable for 3D modeling, animation, skeleton based tracking applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge