Yidong Cheng
A Masked Image Reconstruction Network for Document-level Relation Extraction
Apr 21, 2022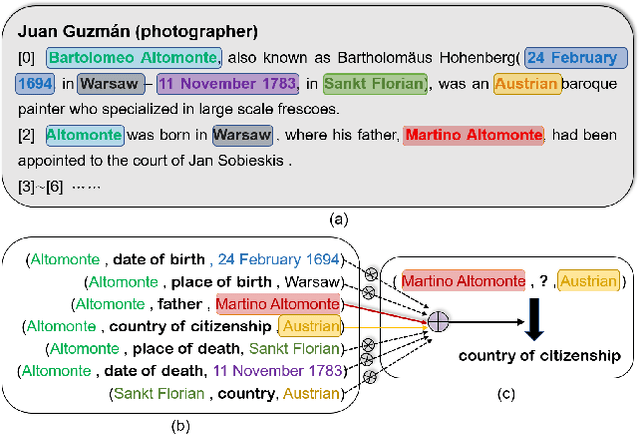


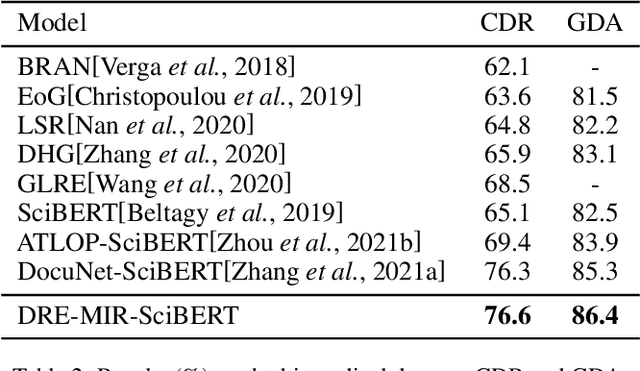
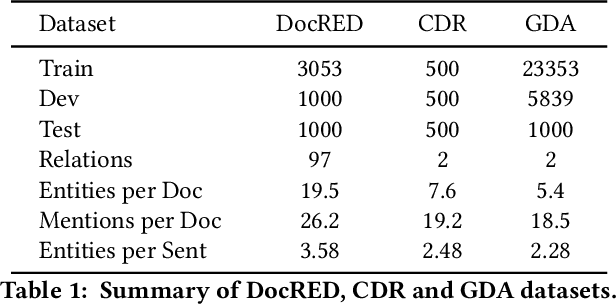
Abstract:Document-level relation extraction aims to extract relations among entities within a document. Compared with its sentence-level counterpart, Document-level relation extraction requires inference over multiple sentences to extract complex relational triples. Previous research normally complete reasoning through information propagation on the mention-level or entity-level document-graphs, regardless of the correlations between the relationships. In this paper, we propose a novel Document-level Relation Extraction model based on a Masked Image Reconstruction network (DRE-MIR), which models inference as a masked image reconstruction problem to capture the correlations between relationships. Specifically, we first leverage an encoder module to get the features of entities and construct the entity-pair matrix based on the features. After that, we look on the entity-pair matrix as an image and then randomly mask it and restore it through an inference module to capture the correlations between the relationships. We evaluate our model on three public document-level relation extraction datasets, i.e. DocRED, CDR, and GDA. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on these three datasets and has excellent robustness against the noises during the inference process.
NC-DRE: Leveraging Non-entity Clue Information for Document-level Relation Extraction
Apr 01, 2022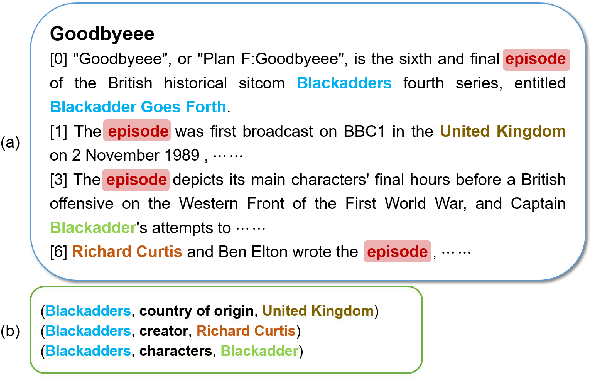

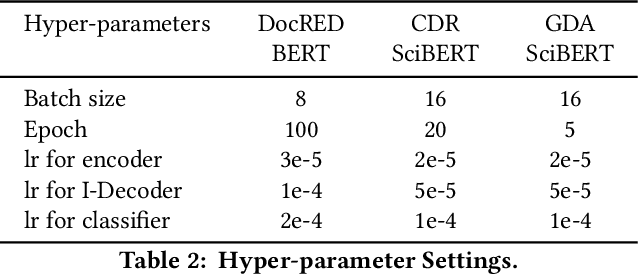
Abstract:Document-level relation extraction (RE), which requires reasoning on multiple entities in different sentences to identify complex inter-sentence relations, is more challenging than sentence-level RE. To extract the complex inter-sentence relations, previous studies usually employ graph neural networks (GNN) to perform inference upon heterogeneous document-graphs. Despite their great successes, these graph-based methods, which normally only consider the words within the mentions in the process of building graphs and reasoning, tend to ignore the non-entity clue words that are not in the mentions but provide important clue information for relation reasoning. To alleviate this problem, we treat graph-based document-level RE models as an encoder-decoder framework, which typically uses a pre-trained language model as the encoder and a GNN model as the decoder, and propose a novel graph-based model NC-DRE that introduces decoder-to-encoder attention mechanism to leverage Non-entity Clue information for Document-level Relation Extraction.
A Densely Connected Criss-Cross Attention Network for Document-level Relation Extraction
Mar 26, 2022



Abstract:Document-level relation extraction (RE) aims to identify relations between two entities in a given document. Compared with its sentence-level counterpart, document-level RE requires complex reasoning. Previous research normally completed reasoning through information propagation on the mention-level or entity-level document-graph, but rarely considered reasoning at the entity-pair-level.In this paper, we propose a novel model, called Densely Connected Criss-Cross Attention Network (Dense-CCNet), for document-level RE, which can complete logical reasoning at the entity-pair-level. Specifically, the Dense-CCNet performs entity-pair-level logical reasoning through the Criss-Cross Attention (CCA), which can collect contextual information in horizontal and vertical directions on the entity-pair matrix to enhance the corresponding entity-pair representation. In addition, we densely connect multiple layers of the CCA to simultaneously capture the features of single-hop and multi-hop logical reasoning.We evaluate our Dense-CCNet model on three public document-level RE datasets, DocRED, CDR, and GDA. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on these three datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge