Xuening Yuan
DreamScape: 3D Scene Creation via Gaussian Splatting joint Correlation Modeling
Apr 14, 2024
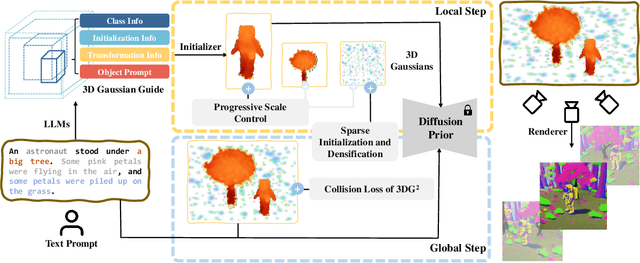
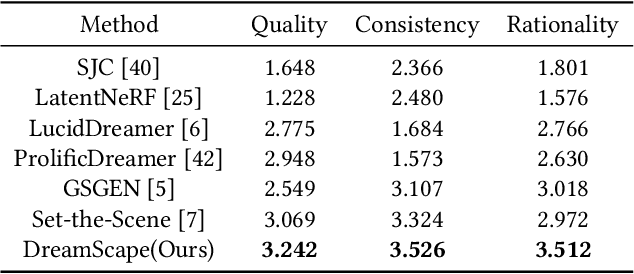
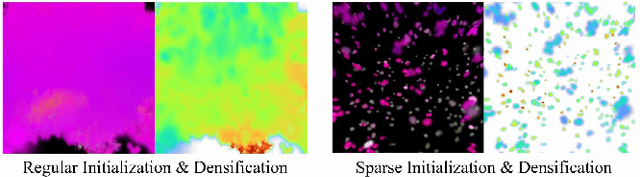
Abstract:Recent progress in text-to-3D creation has been propelled by integrating the potent prior of Diffusion Models from text-to-image generation into the 3D domain. Nevertheless, generating 3D scenes characterized by multiple instances and intricate arrangements remains challenging. In this study, we present DreamScape, a method for creating highly consistent 3D scenes solely from textual descriptions, leveraging the strong 3D representation capabilities of Gaussian Splatting and the complex arrangement abilities of large language models (LLMs). Our approach involves a 3D Gaussian Guide ($3{DG^2}$) for scene representation, consisting of semantic primitives (objects) and their spatial transformations and relationships derived directly from text prompts using LLMs. This compositional representation allows for local-to-global optimization of the entire scene. A progressive scale control is tailored during local object generation, ensuring that objects of different sizes and densities adapt to the scene, which addresses training instability issue arising from simple blending in the subsequent global optimization stage. To mitigate potential biases of LLM priors, we model collision relationships between objects at the global level, enhancing physical correctness and overall realism. Additionally, to generate pervasive objects like rain and snow distributed extensively across the scene, we introduce a sparse initialization and densification strategy. Experiments demonstrate that DreamScape offers high usability and controllability, enabling the generation of high-fidelity 3D scenes from only text prompts and achieving state-of-the-art performance compared to other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge